Basic Concepts in Machine Learning
Machine Learning is continuously growing in the IT world and gaining strength in different business sectors. Although Machine Learning is in the developing phase, it is popular among all technologies. It is a field of study that makes computers capable of automatically learning and improving from experience. Hence, Machine Learning focuses on the strength of computer programs with the help of collecting data from various observations. In this article, ”Concepts in Machine Learning”, we will discuss a few basic concepts used in Machine Learning such as what is Machine Learning, technologies and algorithms used in Machine Learning, Applications and example of Machine Learning, and much more. So, let’s start with a quick introduction to machine learning.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is defined as a technology that is used to train machines to perform various actions such as predictions, recommendations, estimations, etc., based on historical data or past experience.
Machine Learning enables computers to behave like human beings by training them with the help of past experience and predicted data.
There are three key aspects of Machine Learning, which are as follows:
- Task: A task is defined as the main problem in which we are interested. This task/problem can be related to the predictions and recommendations and estimations, etc.
- Experience: It is defined as learning from historical or past data and used to estimate and resolve future tasks.
- Performance: It is defined as the capacity of any machine to resolve any machine learning task or problem and provide the best outcome for the same. However, performance is dependent on the type of machine learning problems.
Techniques in Machine Learning
Machine Learning techniques are divided mainly into the following 4 categories:
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is applicable when a machine has sample data, i.e., input as well as output data with correct labels. Correct labels are used to check the correctness of the model using some labels and tags. Supervised learning technique helps us to predict future events with the help of past experience and labeled examples. Initially, it analyses the known training dataset, and later it introduces an inferred function that makes predictions about output values. Further, it also predicts errors during this entire learning process and also corrects those errors through algorithms.
Example: Let’s assume we have a set of images tagged as ”dog”. A machine learning algorithm is trained with these dog images so it can easily distinguish whether an image is a dog or not.
2. Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, a machine is trained with some input samples or labels only, while output is not known. The training information is neither classified nor labeled; hence, a machine may not always provide correct output compared to supervised learning.
Although Unsupervised learning is less common in practical business settings, it helps in exploring the data and can draw inferences from datasets to describe hidden structures from unlabeled data.
Example: Let’s assume a machine is trained with some set of documents having different categories (Type A, B, and C), and we have to organize them into appropriate groups. Because the machine is provided only with input samples or without output, so, it can organize these datasets into type A, type B, and type C categories, but it is not necessary whether it is organized correctly or not.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning is a feedback-based machine learning technique. In such type of learning, agents (computer programs) need to explore the environment, perform actions, and on the basis of their actions, they get rewards as feedback. For each good action, they get a positive reward, and for each bad action, they get a negative reward. The goal of a Reinforcement learning agent is to maximize the positive rewards. Since there is no labeled data, the agent is bound to learn by its experience only.
4. Semi-supervised Learning
Semi-supervised Learning is an intermediate technique of both supervised and unsupervised learning. It performs actions on datasets having few labels as well as unlabeled data. However, it generally contains unlabeled data. Hence, it also reduces the cost of the machine learning model as labels are costly, but for corporate purposes, it may have few labels. Further, it also increases the accuracy and performance of the machine learning model.
Sem-supervised learning helps data scientists to overcome the drawback of supervised and unsupervised learning. Speech analysis, web content classification, protein sequence classification, text documents classifiers., etc., are some important applications of Semi-supervised learning.
Applications of Machine Learning
Machine Learning is widely being used in approximately every sector, including healthcare, marketing, finance, infrastructure, automation, etc. There are some important real-world examples of machine learning, which are as follows:
Healthcare and Medical Diagnosis:
Machine Learning is used in healthcare industries that help in generating neural networks. These self-learning neural networks help specialists for providing quality treatment by analyzing external data on a patient’s condition, X-rays, CT scans, various tests, and screenings. Other than treatment, machine learning is also helpful for cases like automatic billing, clinical decision supports, and development of clinical care guidelines, etc.
Marketing:
Machine learning helps marketers to create various hypotheses, testing, evaluation, and analyze datasets. It helps us to quickly make predictions based on the concept of big data. It is also helpful for stock marketing as most of the trading is done through bots and based on calculations from machine learning algorithms. Various Deep Learning Neural network helps to build trading models such as Convolutional Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network, Long-short term memory, etc.
Self-driving cars:
This is one of the most exciting applications of machine learning in today’s world. It plays a vital role in developing self-driving cars. Various automobile companies like Tesla, Tata, etc., are continuously working for the development of self-driving cars. It also becomes possible by the machine learning method (supervised learning), in which a machine is trained to detect people and objects while driving.
Speech Recognition:
Speech Recognition is one of the most popular applications of machine learning. Nowadays, almost every mobile application comes with a voice search facility. This ”Search By Voice” facility is also a part of speech recognition. In this method, voice instructions are converted into text, which is known as Speech to text” or “Computer speech recognition.
Google assistant, SIRI, Alexa, Cortana, etc., are some famous applications of speech recognition.
Traffic Prediction:
Machine Learning also helps us to find the shortest route to reach our destination by using Google Maps. It also helps us in predicting traffic conditions, whether it is cleared or congested, through the real-time location of the Google Maps app and sensor.
Image Recognition:
Image recognition is also an important application of machine learning for identifying objects, persons, places, etc. Face detection and auto friend tagging suggestion is the most famous application of image recognition used by Facebook, Instagram, etc. Whenever we upload photos with our Facebook friends, it automatically suggests their names through image recognition technology.
Product Recommendations:
Machine Learning is widely used in business industries for the marketing of various products. Almost all big and small companies like Amazon, Alibaba, Walmart, Netflix, etc., are using machine learning techniques for products recommendation to their users. Whenever we search for any products on their websites, we automatically get started with lots of advertisements for similar products. This is also possible by Machine Learning algorithms that learn users’ interests and, based on past data, suggest products to the user.
Automatic Translation:
Automatic language translation is also one of the most significant applications of machine learning that is based on sequence algorithms by translating text of one language into other desirable languages. Google GNMT (Google Neural Machine Translation) provides this feature, which is Neural Machine Learning. Further, you can also translate the selected text on images as well as complete documents through Google Lens.
Virtual Assistant:
A virtual personal assistant is also one of the most popular applications of machine learning. First, it records out voice and sends to cloud-based server then decode it with the help of machine learning algorithms. All big companies like Amazon, Google, etc., are using these features for playing music, calling someone, opening an app and searching data on the internet, etc.
Email Spam and Malware Filtering:
Machine Learning also helps us to filter various Emails received on our mailbox according to their category, such as important, normal, and spam. It is possible by ML algorithms such as Multi-Layer Perceptron, Decision tree, and Naïve Bayes classifier.
Commonly used Machine Learning Algorithms
Here is a list of a few commonly used Machine Learning Algorithms as follows:
Linear Regression
Linear Regression is one of the simplest and popular machine learning algorithms recommended by a data scientist. It is used for predictive analysis by making predictions for real variables such as experience, salary, cost, etc.
It is a statistical approach that represents the linear relationship between two or more variables, either dependent or independent, hence called Linear Regression. It shows the value of the dependent variable changes with respect to the independent variable, and the slope of this graph is called as Line of Regression.
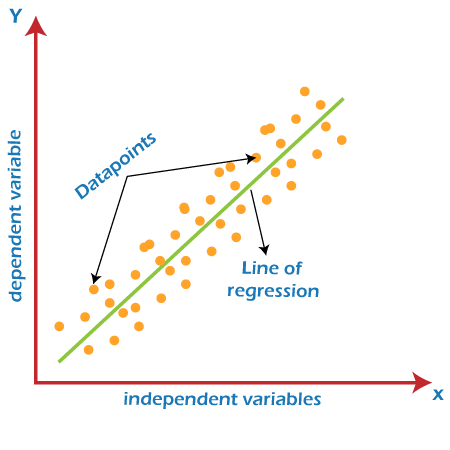
Linear Regression can be expressed mathematically as follows:
y= a0+a1x+ ε
Y= Dependent Variable
X= Independent Variable
a0= intercept of the line (Gives an additional degree of freedom)
a1 = Linear regression coefficient (scale factor to each input value).
ε = random error
The values for x and y variables are training datasets for Linear Regression model representation.
Types of Linear Regression:
- Simple Linear Regression
- Multiple Linear Regression
Applications of Linear Regression:
Linear Regression is helpful for evaluating the business trends and forecasts such as prediction of salary of a person based on their experience, prediction of crop production based on the amount of rainfall, etc.
Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression is a subset of the Supervised learning technique. It helps us to predict the output of categorical dependent variables using a given set of independent variables. However, it can be Binary (0 or 1) as well as Boolean (true/false), but instead of giving an exact value, it gives a probabilistic value between o or 1. It is much similar to Linear Regression, depending on its use in the machine learning model. As Linear regression is used for solving regression problems, similarly, Logistic regression is helpful for solving classification problems.
Logistic Regression can be expressed as an ‘S-shaped curve called sigmoid functions. It predicts two maximum values (0 or 1).
Mathematically, we can express Logistic regression as follows:
Types of Logistic Regression:
- Binomial
- Multinomial
- Ordinal
K Nearest Neighbour (KNN)
It is also one of the simplest machine learning algorithms that come under supervised learning techniques. It is helpful for solving regression as well as classification problems. It assumes the similarity between the new data and available data and puts the new data into the category that is most similar to the available categories. It is also known as Lazy Learner Algorithms because it does not learn from the training set immediately; instead, it stores the dataset, and at the time of classification, it performs an action on the dataset. Let’s suppose we have a few sets of images of cats and dogs and want to identify whether a new image is of a cat or dog. Then KNN algorithm is the best way to identify the cat from available data sets because it works on similarity measures. Hence, the KNN model will compare the new image with available images and put the output in the cat’s category.
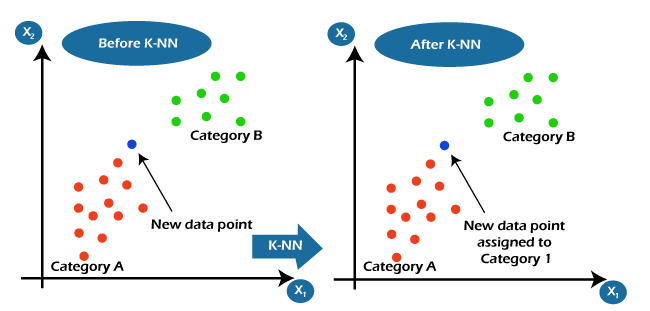
Let’s understand the KNN algorithm with the below screenshot, where we have to assign a new data point based on the similarity with available data points.
Applications of KNN algorithm in Machine Learning
Including Machine Learning, KNN algorithms are used in so many fields as follows:
- Healthcare and Medical diagnosis
- Credit score checking
- Text Editing
- Hotel Booking
- Gaming
- Natural Language Processing, etc.
K-Means Clustering
K-Means Clustering is a subset of unsupervised learning techniques. It helps us to solve clustering problems by means of grouping the unlabeled datasets into different clusters. Here K defines the number of pre-defined clusters that need to be created in the process, as if K=2, there will be two clusters, and for K=3, there will be three clusters, and so on.
Decision Tree
Decision Tree is also another type of Machine Learning technique that comes under Supervised Learning. Similar to KNN, the decision tree also helps us to solve classification as well as regression problems, but it is mostly preferred to solve classification problems. The name decision tree is because it consists of a tree-structured classifier in which attributes are represented by internal nodes, decision rules are represented by branches, and the outcome of the model is represented by each leaf of a tree. The tree starts from the decision node, also known as the root node, and ends with the leaf node.
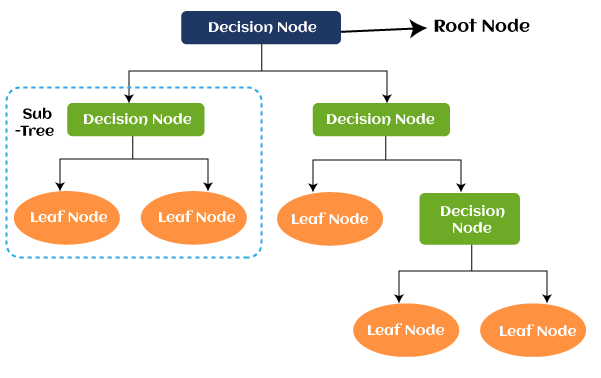
Decision nodes help us to make any decision, whereas leaves are used to determine the output of those decisions.
A Decision Tree is a graphical representation for getting all the possible outcomes to a problem or decision depending on certain given conditions.
Random Forest
Random Forest is also one of the most preferred machine learning algorithms that come under the Supervised Learning technique. Similar to KNN and Decision Tree, It also allows us to solve classification as well as regression problems, but it is preferred whenever we have a requirement to solve a complex problem and to improve the performance of the model.
A random forest algorithm is based on the concept of ensemble learning, which is a process of combining multiple classifiers.
Random forest classifier is made from a combination of a number of decision trees as well as various subsets of the given dataset. This combination takes input as an average prediction from all trees and improves the accuracy of the model. The greater number of trees in the forest leads to higher accuracy and prevents the problem of overfitting. Further, It also takes less training time as compared to other algorithms.
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
It is also one of the most popular machine learning algorithms that come as a subset of the Supervised Learning technique in machine learning. The goal of the support vector machine algorithm is to create the best line or decision boundary that can segregate n-dimensional space into classes so that we can easily put the new data point in the correct category in the future. This best decision boundary is called a hyperplane. It is also used to solve classification as well as regression problems. It is used for Face detection, image classification, text categorization, etc.
Naïve Bayes
The naïve Bayes algorithm is one of the simplest and most effective machine learning algorithms that come under the supervised learning technique. It is based on the concept of the Bayes Theorem, used to solve classification-related problems. It helps to build fast machine learning models that can make quick predictions with greater accuracy and performance. It is mostly preferred for text classification having high-dimensional training datasets.
It is used as a probabilistic classifier which means it predicts on the basis of the probability of an object. Spam filtration, Sentimental analysis, and classifying articles are some important applications of the Naïve Bayes algorithm.
It is also based on the concept of Bayes Theorem, which is also known as Bayes’ Rule or Bayes’ law. Mathematically, Bayes Theorem can be expressed as follows:
Where,
- P(A) is Prior Probability
- P(B) is Marginal Probability
- P(A|B) is Posterior probability
- P(B|A) is Likelihood probability
Difference between machine learning and Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial intelligence is a technology using which we can create intelligent systems that can simulate human intelligence, whereas Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, which enables machines to learn from past data or experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence is a technology used to create an intelligent system that enables a machine to simulate human behavior. Whereas, Machine Learning is a branch of AI which helps a machine to learn from experience without being explicitly programmed.
- AI helps to make humans like intelligent computer systems to solve complex problems. Whereas, ML is used to gain accurate predictions from past data or experience.
- AI can be divided into Weak AI, General AI, and Strong AI. Whereas, IML can be divided into Supervised learning, Unsupervised learning, and Reinforcement learning.
- Each AI agent includes learning, reasoning, and self-correction. Each ML model includes learning and self-correction when introduced with new data.
- AI deals with Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. ML deals with Structured and semi-structured data.
- Applications of AI: Siri, customer support using catboats, Expert System, Online game playing, an intelligent humanoid robot, etc. Applications of ML: Online recommender system, Google search algorithms, Facebook auto friend tagging suggestions, etc.
Conclusion
This article has introduced you to a few important basic concepts of Machine Learning. Now, we can say, machine learning helps to build a smart machine that learns from past experience and works faster. There are a lot of online games available on the internet that are much faster than a real game player, such as Chess, AlphaGo and Ludo, etc. However, machine learning is a broad concept, but also you can learn each concept in a few hours of study. If you are preparing yourself for making a data scientist or machine learning engineer, then you must have in-depth knowledge of each concept of machine learning.
