Scan Conversion Definition
It is a process of representing graphics objects a collection of pixels. The graphics objects are continuous. The pixels used are discrete. Each pixel can have either on or off state.
The circuitry of the video display device of the computer is capable of converting binary values (0, 1) into a pixel on and pixel off information. 0 is represented by pixel off. 1 is represented using pixel on. Using this ability graphics computer represent picture having discrete dots.
Any model of graphics can be reproduced with a dense matrix of dots or points. Most human beings think graphics objects as points, lines, circles, ellipses. For generating graphical object, many algorithms have been developed.
Advantage of developing algorithms for scan conversion
- Algorithms can generate graphics objects at a faster rate.
- Using algorithms memory can be used efficiently.
- Algorithms can develop a higher level of graphical objects.
Examples of objects which can be scan converted
- Point
- Line
- Sector
- Arc
- Ellipse
- Rectangle
- Polygon
- Characters
- Filled Regions
The process of converting is also called as rasterization. The algorithms implementation varies from one computer system to another computer system. Some algorithms are implemented using the software. Some are performed using hardware or firmware. Some are performed using various combinations of hardware, firmware, and software.
Pixel or Pel:
The term pixel is a short form of the picture element. It is also called a point or dot. It is the smallest picture unit accepted by display devices. A picture is constructed from hundreds of such pixels. Pixels are generated using commands. Lines, circle, arcs, characters; curves are drawn with closely spaced pixels. To display the digit or letter matrix of pixels is used.
The closer the dots or pixels are, the better will be the quality of picture. Closer the dots are, crisper will be the picture. Picture will not appear jagged and unclear if pixels are closely spaced. So the quality of the picture is directly proportional to the density of pixels on the screen.
Pixels are also defined as the smallest addressable unit or element of the screen. Each pixel can be assigned an address as shown in fig:
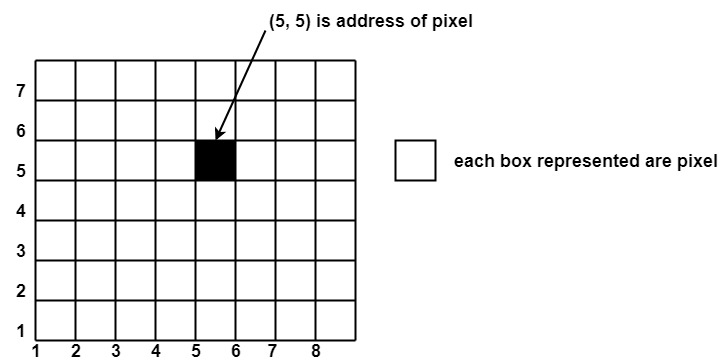
Different graphics objects can be generated by setting the different intensity of pixels and different colors of pixels. Each pixel has some co-ordinate value. The coordinate is represented using row and column.
P (5, 5) used to represent a pixel in the 5th row and the 5th column. Each pixel has some intensity value which is represented in memory of computer called a frame buffer. Frame Buffer is also called a refresh buffer. This memory is a storage area for storing pixels values using which pictures are displayed. It is also called as digital memory. Inside the buffer, image is stored as a pattern of binary digits either 0 or 1. So there is an array of 0 or 1 used to represent the picture. In black and white monitors, black pixels are represented using 1’s and white pixels are represented using 0’s. In case of systems having one bit per pixel frame buffer is called a bitmap. In systems with multiple bits per pixel it is called a pixmap.
