Difference Between Data Science and Machine Learning
Data Science is the study of data cleansing, preparation, and analysis, while machine learning is a branch of AI and subfield of data science. Data Science and Machine Learning are the two popular modern technologies, and they are growing with an immoderate rate. But these two buzzwords, along with artificial intelligence and deep learning are very confusing term, so it is important to understand how they are different from each other. In this topic, we will understand the difference between Data Science and Machine Learning only, and how they relate to each other.
Data Science and Machine Learning are closely related to each other but have different functionalities and different goals. At a glance, Data Science is a field to study the approaches to find insights from the raw data. Whereas, Machine Learning is a technique used by the group of data scientists to enable the machines to learn automatically from the past data. To understand the difference in-depth, let’s first have a brief introduction to these two technologies.
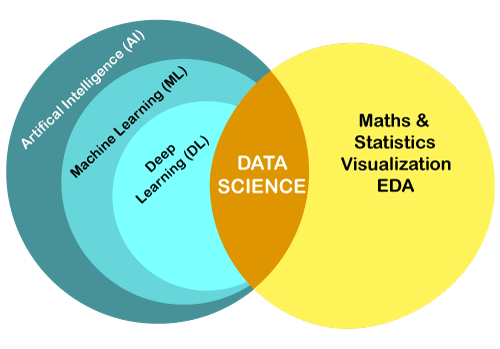
Note: Data Science and Machine Learning are closely related to each other but cannot be treated as synonyms.
What is Data Science?
Data science, as its name suggests, is all about the data. Hence, we can define it as, “A field of deep study of data that includes extracting useful insights from the data, and processing that information using different tools, statistical models, and Machine learning algorithms.” It is a concept that is used to handle big data that includes data cleaning, data preparation, data analysis, and data visualization.
A data scientist collects the raw data from various sources, prepares and pre-processes the data, and applies machine learning algorithms, predictive analysis to extract useful insights from the collected data.
For example, Netflix uses data science techniques to understand user interest by mining the data and viewing patterns of its users.
Skills Required to become Data Scientist
- An excellent programming knowledge of Python, R, SAS, or Scala.
- Experience in SQL database Coding.
- Knowledge of Machine Learning Algorithms.
- Deep Knowledge of Statistics concepts.
- Data Mining, cleaning, and Visualizing skills.
- Skills to use Big data tools such as Hadoop.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence and the subfield of Data Science. It is a growing technology that enables machines to learn from past data and perform a given task automatically. It can be defined as:
Machine Leaning allows the computers to learn from the past experiences by its own, it uses statistical methods to improve the performance and predict the output without being explicitly programmed.
The popular applications of ML are Email spam filtering, product recommendations, online fraud detection, etc.
Skills Needed for the Machine Learning Engineer:
- Understanding and implementation of Machine Learning Algorithms.
- Natural Language Processing.
- Good Programming knowledge of Python or R.
- Knowledge of Statistics and probability concepts.
- Knowledge of data modeling and data evaluation.
Where is Machine Learning used in Data Science?
The use of machine learning in data science can be understood by the development process or life cycle of Data Science. The different steps that occur in Data science lifecycle are as follows:
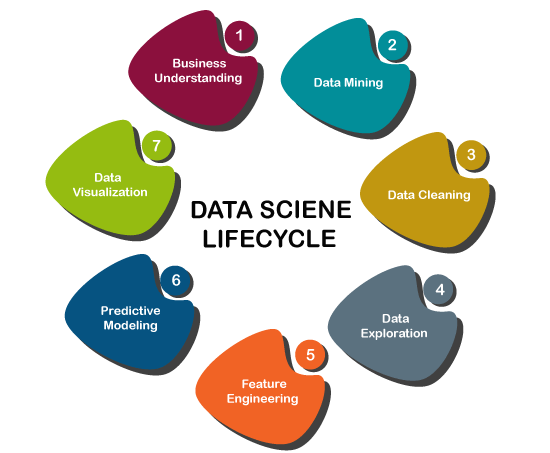
- Business Requirements: In this step, we try to understand the requirement for the business problem for which we want to use it. Suppose we want to create a recommendation system, and the business requirement is to increase sales.
- Data Acquisition: In this step, the data is acquired to solve the given problem. For the recommendation system, we can get the ratings provided by the user for different products, comments, purchase history, etc.
- Data Processing: In this step, the raw data acquired from the previous step is transformed into a suitable format, so that it can be easily used by the further steps.
- Data Exploration: It is a step where we understand the patterns of the data, and try to find out the useful insights from the data.
- Modeling: The data modeling is a step where machine learning algorithms are used. So, this step includes the whole machine learning process. The machine learning process involves importing the data, data cleaning, building a model, training the model, testing the model, and improving the model’s efficiency.
- Deployment & Optimization: This is the last step where the model is deployed on an actual project, and the performance of the model is checked.
Comparison Between Data Science and Machine Learning
The below table describes the basic differences between Data Science and ML:
| Data Science | Machine Learning |
|---|---|
| It deals with understanding and finding hidden patterns or useful insights from the data, which helps to take smarter business decisions. | It is a subfield of data science that enables the machine to learn from the past data and experiences automatically. |
| It is used for discovering insights from the data. | It is used for making predictions and classifying the result for new data points. |
| It is a broad term that includes various steps to create a model for a given problem and deploy the model. | It is used in the data modeling step of the data science as a complete process. |
| A data scientist needs to have skills to use big data tools like Hadoop, Hive and Pig, statistics, programming in Python, R, or Scala. | Machine Learning Engineer needs to have skills such as computer science fundamentals, programming skills in Python or R, statistics and probability concepts, etc. |
| It can work with raw, structured, and unstructured data. | It mostly requires structured data to work on. |
| Data scientists spent lots of time in handling the data, cleansing the data, and understanding its patterns. | ML engineers spend a lot of time for managing the complexities that occur during the implementation of algorithms and mathematical concepts behind that. |
