Diagonal formula
Diagonal is a slanting line intersecting the opposite angles of any figure. It joins two opposite corners of a square, rectangle, cube, cuboid, or polygon. A diagonal formula is used to find the diagonal length of different figures related to their sides.
For example,
The diagonal formula to find the length of the square is √ 2 a. If the side of the square (a) is known, we can easily find the length of its diagonal.
Let’s discuss the diagonal formula of parallelograms, cubes, cuboids, and polygons.
Parallelograms
A diagonal divides a parallelogram into two equal triangles. It has only two diagonals that intersect each other at the center point. A diagonal also divides the angle formed between the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram.
A parallelogram ABCD is shown below:
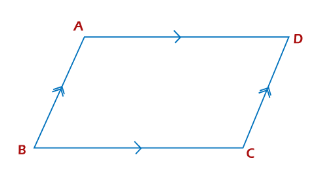
The properties of a parallelogram are as follows:
- Opposite sides equal
- Opposite angle equal
- Sum of all internal angles in 360 degrees
- Diagonals intersect each other
The parameters of a parallelogram are given by:
Length = a
Width = b
Diagonals = M and N
Alpha (α) = Angle between the two adjacent sides
Beta (β) = Angle between the two intersecting diagonals
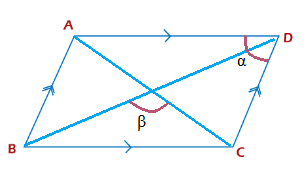
Case 1: Diagonal formula in terms of cosine Beta angle
M = √ (a2 + b2 – 2abcosβ)
N = √ (a2 + b2 + 2abcosβ)
Case 2: Diagonal formula in terms of cosine Alpha angle
M = √ (a2 + b2 – 2abcosα)
N = √ (a2 + b2 + 2abcosα)
Case 2: Diagonal formula in terms of two sides and other diagonal
M = √ (2a2 + 2b2 – N2)
N = √ (2a2 + 2b2 – M2)
Types of parallelogram
There are three types of parallelogram, square, rectangle, and rhombus.
Square
A square has four sides of equal length. A diagonal divides the square into two equal right-angled triangles. The diagonal of the square can be calculated by applying the Pythagoras theorem of the right-angle triangle.
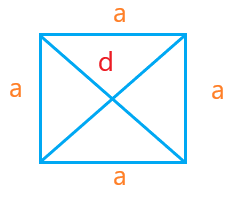
Let the side and diagonal of the square be ‘a’ and ‘d.’
The formula to calculate the diagonal of square using Pythagoras theorem is given by:
Square of diagonal = square of length + square of width
Hypotenuse2 = base2 + height2
The sides of square are equal, i.e., length = width = a
d2 = a2 + a2
d = √ 2 a2
d = a √ 2
Rectangle
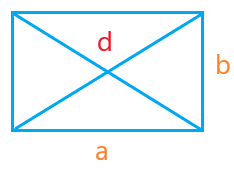
A rectangle has four sides where its two opposite sides are equal. It has two pairs of opposite sides. One pair of opposite sides is longer than the other pair. A diagonal divides the rectangle into two equal right-angle triangles.
Let the dimensions of rectangle be:
Length = l
Width = b
Diagonal = d
The formula to calculate the diagonal of rectangle using Pythagoras theorem is given by:
Square of diagonal = square of length + square of width
Hypotenuse2 = base2 + height2
d2 = a2 + b2
d = √ (a2 + b2)
Rhombus
A rhombus also has four sides, with all sides equal. A diagonal divides the rectangle into two equal right-angled triangles. It has two diagonals that intersect each other at the center.
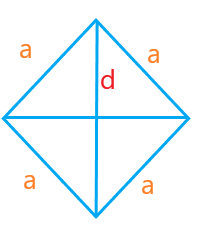
Let the side and diagonal of the rhombus be ‘a’ and ‘d.’
The formula to calculate the diagonal of rhombus using Pythagoras theorem is given by:
Square of diagonal = square of length + square of width
Hypotenuse2 = base2 + height2
The sides of rhombus are equal, i.e., length = width = a
d2 = a2 + a2
d = √ 2 a2
d = a √ 2
Cube
A cube is a 3D figure with dimension length, width, and height. A cube has 12 sides and 6 faces. Each face of a cube has two diagonals. Parallelograms are the 2D figures and thus have only one face with two diagonals. All the sides of a cube are equal. Hence, all the diagonals of the cube are also equal.
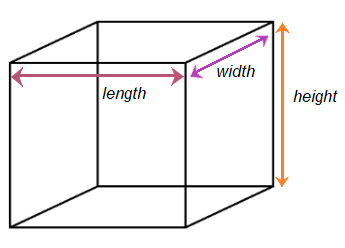
Let the length, width, and height of the cube be ‘a’ and diagonal be ‘d.’
Length = width = height = a
Diagonal = d
Diagonal of the cube is given by:
d2 = a2 + a2 + a2
d = √ (3a2)
d = a√3
Cuboids
Cuboids also have 12 sides, faces, and 12 diagonals. It has three dimensions, length, width, and height. The difference between cube and cuboid is that the three sides of the cube are equal, while that of the cuboid are not equal.

Let the dimensions of cube be:
Length = l
Width = w
Height = h
Diagonal = d
Diagonal of the cuboid is given by:
d2 = l2 + w2 + h2
d = √ (l2 + w2 + h2)
Polygon
A polygon is a figure with three or more than three sides.
The formula to calculate the diagonal of the polygon is given by:
D = n(n – 3)/2
Where,
n = sides of polygon
If n= 3
D = 0
It proves that triangles do not have a diagonal.
The above formula helps us to find the number of diagonals of a polygon with any number of sides.
The number of diagonals of different polygons is listed in the below table:
| S.No | Number of sides of polygon | Number of Diagonals |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 (Quadrilateral) | 2 |
| 2 | 5 (Pentagon) | 5 |
| 3 | 6 (Hexagon) | 9 |
| 4 | 7 (Heptagon) | 14 |
| 5 | 8 (Octagon) | 20 |
| 6 | 9 (Nonagon) | 27 |
| 7 | 10 (Decagon) | 35 |
| 8 | 11 (Hendecagon) | 44 |
Examples
Let’s discuss some examples based on the diagonal formula.
Example 1: Find the diagonal of a square with a side of 4 cm.
Solution: The formula to calculate the diagonal of a square is given by:
d = a √ 2
Where,
d is the diagonal
a is the side of a square
d = a √ 2
d = 4√ 2
d = 5.66 cm
Thus, the diagonal of a square of side 4 cm is 5.66 cm.
Example 2: Find the diagonal of a rectangle with sides of 3m and 4m.
Solution: The formula to calculate the diagonal of a rectangle is given by:
d = √ (a2 + b2)
Where,
a and b are the two adjacent sides of the rectangle
d is the diagonal
d = √ (32 + 42)
d = √ (9 + 16)
d = √25
d = 5m
Thus, the diagonal of a rectangle with sides 3m and 4m is 5m.
Example 3: Find the diagonal of a cube with a side of 2 m.
Solution: The formula to calculate the diagonal of a cube is given by:
d = a√3
Where,
d is the diagonal
a is the side of a cube
d = 2√3
d = 3.46 m
Thus, the diagonal of a cube with side 2 m is 3.46 m.
Example 4: Find the diagonal of rhombus with a side of 10 cm.
The formula to calculate the diagonal of a rhombus is given by:
d = a √ 2
Where,
d is the diagonal
a is the side of a rhombus
d = a √ 2
d = 10√ 2
d = 14.14 cm
Thus, the diagonal of a cube rhombus with side 10 cm is 14.14 cm.
Example 5: Find the diagonal of a cuboid with the sides 4m, 3m, and 2m.
Solution: The formula to calculate the diagonal of a cuboid is given by:
d = √ (l2 + w2 + h2)
Where,
l, w, and h are the length, width, and height of the cuboid
d is the diagonal
d = √ (42 + 32 + 22)
d = √ (16 + 9 + 4)
d = √29
d = 5.38 m
Thus, the diagonal of a cuboid with side 4m, 3m, and 2m is 5.38m.
Example 6: Find the diagonal of a rectangle with sides 12m and 500cm.
Solution: The formula to calculate the diagonal of a rectangle is given by:
d = √ (a2 + b2)
Where,
a and b are the two adjacent sides of the rectangle
d is the diagonal
But, the sides of rectangle are given in different units. We need to convert the sides into the same units.
a = 12m
b = 500 cm = 5/100 = 5m
(1m = 100cm)
d = √ (122 + 52)
d = √ (144 + 25)
d = √169
d = 13 m
Or
a = 12m = 1200 cm
b = 500 cm
(1m = 100cm)
d = √ (12002 + 5002)
d = √ (1440000 + 250000)
d = √1690000
d = 1300 cm
Example 7: What is the diagonal length of a parallelogram of sides 5m and 6m and a 60° angle between the two adjacent sides?
Solution: Formula to find the diagonal length of parallelogram is:
P = √ (a2 + b2 – 2abcosα)
Q = √ (a2 + b2 + 2abcosα)
L = 5m
W = 6m
A = 60°
P = √ (52 + 62 – 2×5×6×cos60)
P = √ (25 + 36 – 2×5×6×1/2)
P = √ (25 + 36 – 30)
P = √31
P = 5.56 m
Q = √ (a2 + b2 + 2abcosα)
Q = √ (52 + 62 + 2×5×6×cos60)
Q = √ (25 + 36 + 2×5×6×1/2)
Q = √ (25 + 36 + 30)
Q = √31
Q = 9.54 m
Thus, the lengths of two diagonals of a parallelogram are 5.56m and 9.54m.
