range() Vs. Xrange() Python
In this article, we will discuss what is range() and xrange() function, how they are used in Python, and what are the essential features of each.
The functions available in Python can be used in multiple parts of our program since they reduce the size of code and add a lot of value to the readability of code.
First, we will have a look at what is the range function and discuss some programs that involve its usage.
Similarly, then we will understand what is xrange function and get an idea of it with the help of some programs.
At last, we will look at the features of each.
The range() Function-
In the following example, we will print the first 7 numbers starting from 0 to 6. We have specified the value in the range function for the same and provided a space in the end parameter so that it prints the values with space.
The following program illustrates the same-
Example –
Output:

In the second example, we will do the same thing again, that is, print the first 7 numbers starting from 0 to 6. We have specified the value in the range function for the same and provided a space in the end parameter so that it prints the values with space.
After this, we will also check that what type does it return.
The following program illustrates the same-
Example – 2
Output:

In the next example, we have defined a list that contains 10 elements. We have specified the value as the length of our list ‘a’ in the range function for the same and provided a space in the end parameter so that it prints the values with a space.
The following program illustrates the same-
Example – 3
Output:
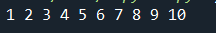
In the next example, we will print the values in the reverse order that lies in the range of 0 to 10. We have specified the value in the range function in the format of start, stop and end. Let us have a look at each one of denote-
start-The value from which we would like to start displaying the elements.
stop- The value on which we would like to stop displaying the elements.
step- The step value refers to the value that indicates the kind of sequence we expect in our results. By default, the value of the step is 0.
The following program illustrates the same-
Example – 4
Output:
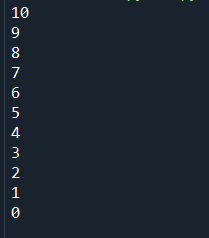
In the next example, we will print the numbers starting from 21 to 31 but this time using the reversed method of Python. We have specified the value in the range function for the same and provided a space in the end parameter so that it prints the values with space.
The following program illustrates the same-
Example – 4
Output:
The Xrange() Function
The xrange() function has the same purpose and returns a generator object but was used in the versions that came before Python 3.
The syntax of xrange is the same as range() which means in xrange also we have to specify start, stop and step.
If you are using Python 3 and execute a program using xrange then it will generate an error since this version onwards range() is used.
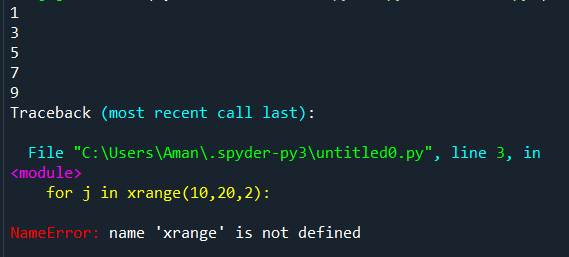
Let’s see what happens when we run the following program in Python-
Example –
Output:
Comparison between Range() AND Xrange()
Here we will compare both based on consumption of memory, return type, speed and operations-
| Parameters | Range() | Xrange() |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Consumption of Memory | Since range() returns a list of elements, it takes more memory. | In comparison to range(), it takes less memory. |
| 2. Return type | It returns a list of integers. | It returns a generator object. |
| 3. Speed | Its execution speed is slower. | Its execution speed is faster. |
| 4. Operations | Since it returns a list, all kinds of arithmetic operations can be performed. | Such operations cannot be performed on xrange(). |
