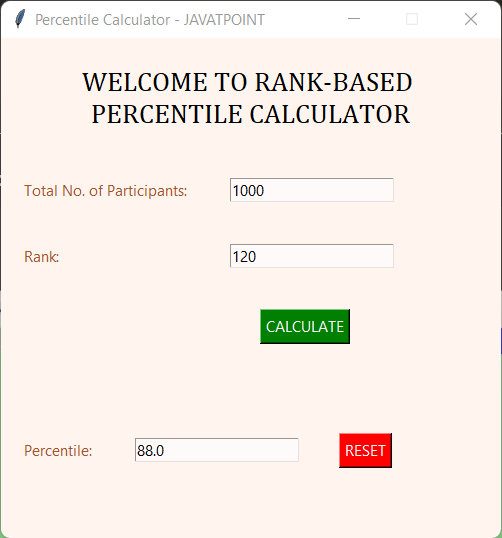
Rank-based Percentile GUI Calculator in Python
Programming language like Python provides various options to develop a Graphical User Interface, abbreviated as GUI. Among these methods used for GUI, Tkinter is the most widely utilized library. In the following tutorial, we will be creating a GUI application to calculate the Percentile on the basis of Rank with the help of the Tkinter library in Python.
Before, let us briefly understand what Percentile means.
What is Percentile?
A percentile is a statistical indicator generally utilized to identify a certain segment of a sample population. In a more precise way, we utilize a percentile to indicate the value (of the variable under consideration) below which a particular percentage of the sample population falls. For instance, if we consider the height distribution of all the English people living in the United Kingdom; by saying that the height value of 175 cm recognizes the 60th Percentile, it implies that the 60% of all the English people living in the United Kingdom are shorter than 175 cm. As we can imagine, percentiles are generally utilized in lots of statistical studies and when reporting results of surveys or measurements on large populations.
How to Calculate Percentiles?
Suppose that we have collected the height of n = 69 people. In order to evaluate the percentiles referred to in this distribution, the first step is to sort all the values in ascending order. At this point, let us assume we are asked to calculate the 65th Percentile of the distribution. We will calculate the so-called rank k = percentile/100. In the following case, k = 65/100 = 0.65. Now we must multiply the rank for the total number of samples in the distribution (n, in the following 67); we obtain k x n = 0.65 x 69 = 44.85. Since the result is not a whole number, we approximate the value to the nearest whole number (45 in this case). In the next step, we will find the height value corresponding to the 45th position within the sample distribution; that value corresponds to the 65th Percentile. In the following case, the result of k x n is a whole number. We process further by directly finding the corresponding value in the sample distribution; that is already our Percentile.
Now, let us start building the project using Tkinter in Python
Building the Rank-based Percentile GUI Calculator using Tkinter
The approach of building the Rank-based Percentile GUI Calculator with the help of the Tkinter library in Python is divided into different steps for better understanding. These steps are as follows:
Step 1: We will start by importing the Tkinter library.
Step 2: We will then define the necessary functions for the project.
Step 3: We will then create the main window (container).
Step 4: We will then add any number of widgets to the main window.
Let us now understand the implementation of these steps in detail.
Importing the required libraries
We will start by importing the Tkinter library. This library will allow us to build the Graphical User Interface in Python.
Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the implementation of the above statement.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have imported all the widgets and methods from the Tkinter library required in this project.
Defining the required functions
Once we have imported the required libraries and modules, we will define the functions necessary for the project. These functions include the function to reset all the entries in the entry fields and the function to calculate the percentile for the given data.
Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the implementation of the above statement.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, the first function we have defined is reset(). Within this function, we have used the delete() method and deleted the entries in all the entry fields. We have then used the focus_set() method on the total_participants_field field and set the cursor focus on that field.
Next function we have defined is calculate_percentile(). We deleted the previous result, if any, within this function, displayed on the percentile_field field. We have then retrieved the values from the entry fields like total_participants_field and rank_field using the get() method and stored them in the students and rank variables. We then calculated the percentile for the given data and rounded off the resultant to 3 decimals using the round() method. At last, we have used the insert() method to insert the resultant value in the percentile_field field.
Creating the main window
We will now create the main window to display all the widgets and the data for the users. We will use the Tk() class of the Tkinter library. We will also use some of the Tk() class methods and decorate the main window.
Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the implementation of the above statement.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above code snippet, we created an object of the Tk() class. We have then added the title to the main window using the title() method. We have then defined the size of the main window using the geometry() method. We have also disabled the resizable option for a better User Interface with the help of the resizable() method. At last, we have used the configure() method and set the background color to #fff5ee.
Adding the Widgets to the main window
Now that we have created the main window for the application, it is time for us to add some widgets to display the data for the users.
We will start by adding some frames to the main window. These frames will be responsible for grouping and organizing the other widgets like Labels, Entry Fields, and Buttons. We will use the Frame() widget to create frames.
Let us consider the snippet of code below illustrating the implementation of the Frame() widgets.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have used the Frame() widget and created three frames for the main window. These frames will allow us to organize the heading, labels, entry fields, and the result section. We have then used the pack() method to set the position of these frames in the application.
We will now add a label to the first frame to display the heading in the application. We will use the Label() widget to create the label and set the master widget to the titleFrame. We will also add some text to it and do some decoration using some other parameters.
Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have used the Label() widget to create a label to display the heading for the main window. We have then set its master widget to the titleFrame frame along with the text to be displayed, font style and size, background, and foreground color. We have then used the pack() method and set the value of the expand parameter to True and the fill parameter to both to set the positioning of the label in the frame.
We will now insert other labels into the main window to display the information like Total Participants, Rank, and Percentile.
Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same:
File: percentileCalculator.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have defined three labels as total_participants_label, rank_label, and percentile_label with the help of the Label() widget. We have set the master widget of the total_participants_label and rank_label labels to the fieldFrame frame and the percentile_label label to the resultFrame frame. We have also included the text to be displayed along with the background and foreground color.
We will now set the position of these labels in the main window and their respective frames using the grid() method. This method will allow us to place the widgets in a two-dimensional (2-D) table. The master widget is split into different rows and columns; each cell in the resulting table can hold a widget.
Let us now consider the following snippet of code illustrating the usage of the grid() method.
File: percentileCalculator.py
Explanation:
In the above code snippet, we used the grid() method on the labels we created earlier. We have set the value of the row, column, padx, pady, and sticky parameters in each label’s grid() method.
We will now add some entry fields to the main window with the help of the Entry() widget. This will allow us to enter the data and display the result.
The following is the snippet of code illustrating the implementation of the Entry() widget in the project.
File: percentileCalculator.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have used the Entry() widget to create three entry fields, namely total_participants_field, rank_field, and percentile_field. We have also set the master widget of the total_participants_field and rank_field field to the fieldFrame frame and the percentile_field field to the resultFrame frame. We have also set the background color of these fields to #fffafa.
We will again use the grid() method and set these fields in the rows and columns as per the need.
The following is the snippet of code illustrating the implementation of the grid() method in positioning the fields we created above.
File: percentileCalculator.py
Explanation:
In the above code snippet, we have used the grid() method on the fields we created earlier to place them in 2-D table format. We have defined the values for the row, column, padx, pady, and sticky parameters in the grid() method.
We will now add the buttons to the main window with the help of the Button() widget to execute the functions we created earlier.
Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the implementation of the Button() widget.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have used the Button() widget to create two buttons, respectively. The first button is the CALCULATE button that will call the calculate_percentile function through the command parameter and calculate the percentile for the given data. The second button is the RESET button that will call the reset function through the command parameter to clear all the entries in the entry fields and set the cursor to the total_participant_field field.
We will now use the grid() method and set the positioning of the buttons in a 2-D table format for a better User Interface.
Let us consider the following snippet of code to understand the same.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above code snippet, we have used the grid() method on the buttons we created earlier to place them in 2-D table format. We have defined the values for the row, column, padx, pady, and sticky parameters in the grid() method.
At last, we will use the mainloop() method to run the main window. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the implementation of the mainloop() method.
File: percentileCalci.py
Explanation:
In the above snippet of code, we have used the mainloop() method to run the main window.
Hence, we have successfully created the project to calculate the percentile based on the rank of the participant. We can now save the Python project file and execute the following command to see the result.
Syntax:
Before we see the output, let us see the complete snippet of code of the “Rank-based Percentile Calculator with GUI” project in Python.
The Complete Project Code
The following is the complete snippet of code for the “Rank-based Percentile Calculator with GUI” project in Python.
File: percentileCalci.py
Output: