RSME – Root Mean Square Error in Python
This tutorial will learn about the RSME (Root Mean Square Error) and its implementation in Python. Let’s get started with its brief introduction.
Introduction
RSME (Root mean square error) calculates the transformation between values predicted by a model and actual values. In other words, it is one such error in the technique of measuring the precision and error rate of any machine learning algorithm of a regression problem.
Error metric allows us to track the various matrices’ efficiency and accuracy. These matrices are given below.
- Mean Square Error (MSE)
- Root Mean Square Error (RSME)
- R-square
- Accuracy
- MAPE, etc.
Mean Square Error (MSE)
MSE is a risk method that facilitates us to signify the average squared difference between the predicted and the actual value of a feature or variable. It is calculated using the below method. The syntax is given below.
Syntax –
Parameters –
- y_true – It is an array-like target_values or n_samples.
- y_pred – It is a estimated target values.
- sample_weight (optional) – It represents the sample weight.
- Multioutput {raw_values, uniform_average} – It defines the aggregating of multiple output values. The raw_values returns a complete set of error for multi output input and the uniform_average is an error of all outputs with the uniform weight.
- Squared – True, returns MSE value otherwise returns RSME value.
Returns –
It returns a non-negative floating point value (the best value is 0.0) or an array of floating point values, one for each individual target.
Let’s understand the following example.
Example – 1
Output:
The difference between actual and predicted values: 1.5388307249337076
Example – 2:
Output:
3.15206
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
RMSE is a square root of value gathered from the mean square error function. It helps us plot a difference between the estimate and actual value of a parameter of the model.
Using RSME, we can easily measure the efficiency of the model.
A well-working algorithm is known if its RSME score of less than 180. Anyhow, if the RSME value surpasses 180, we need to apply feature selection and hyper-parameter tuning on the model parameter.
Root Mean Square Error with NumPy module
RSME is a square root of the average squared difference between the predicted and actual value of the variable/feature. Let’s see the following formula.
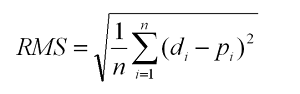
Let’s breakdown the above formula –
- Σ – It represents the “sum”.
- di– It represents the predicted value for the ith
- pi– It represents the predicted value for the ith
- n – It represents the sample size.
We will implement the RSME using the functions of the Numpy module. Let’s understand the following example.
Note – If your system don’t have numpy and sklearn libraries, you can install using the below commands.
Example –
Output:
Root Mean Square Error: 2.127439775880859
Explanation –
We calculated the difference between predicted and actual values in the above program using numpy.subtract() function. First, we defined two lists that contain actual and predicted values. Then we calculated the mean of actual and predicted values difference using the numpy’s squre() method. Finally we calculated the rmse.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have discussed how to calculate root square mean square using Python with illustration of example. It is mostly used to find the accuracy of given dataset. If RSME returns 0; it means there is no difference predicted and observed values.
