Web Services in Cloud Computing
The Internet is the worldwide connectivity of hundreds of thousands of computers belonging to many different networks.
A web service is a standardized method for propagating messages between client and server applications on the World Wide Web. A web service is a software module that aims to accomplish a specific set of tasks. Web services can be found and implemented over a network in cloud computing.
The web service would be able to provide the functionality to the client that invoked the web service.
A web service is a set of open protocols and standards that allow data exchange between different applications or systems. Web services can be used by software programs written in different programming languages and on different platforms to exchange data through computer networks such as the Internet. In the same way, communication on a computer can be inter-processed.
Any software, application, or cloud technology that uses a standardized Web protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) to connect, interoperate, and exchange data messages over the Internet-usually XML (Extensible Markup Language) is considered a Web service. Is.
Web services allow programs developed in different languages to be connected between a client and a server by exchanging data over a web service. A client invokes a web service by submitting an XML request, to which the service responds with an XML response.
- Web services functions
- It is possible to access it via the Internet or intranet network.
- XML messaging protocol that is standardized.
- Operating system or programming language independent.
- Using the XML standard is self-describing.
A simple location approach can be used to detect this.
Web Service Components
XML and HTTP is the most fundamental web service platform. All typical web services use the following components:
1. SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
SOAP stands for “Simple Object Access Protocol”. It is a transport-independent messaging protocol. SOAP is built on sending XML data in the form of SOAP messages. A document known as an XML document is attached to each message.
Only the structure of an XML document, not the content, follows a pattern. The great thing about web services and SOAP is that everything is sent through HTTP, the standard web protocol.
Every SOAP document requires a root element known as an element. In an XML document, the root element is the first element.
The “envelope” is divided into two halves. The header comes first, followed by the body. Routing data, or information that directs the XML document to which client it should be sent, is contained in the header. The real message will be in the body.
2. UDDI (Universal Description, Search, and Integration)
UDDI is a standard for specifying, publishing and searching online service providers. It provides a specification that helps in hosting the data through web services. UDDI provides a repository where WSDL files can be hosted so that a client application can search the WSDL file to learn about the various actions provided by the web service. As a result, the client application will have full access to UDDI, which acts as the database for all WSDL files.
The UDDI Registry will keep the information needed for online services, such as a telephone directory containing the name, address, and phone number of a certain person so that client applications can find where it is.
3. WSDL (Web Services Description Language)
The client implementing the web service must be aware of the location of the web service. If a web service cannot be found, it cannot be used. Second, the client application must understand what the web service does to implement the correct web service. WSDL, or Web Service Description Language, is used to accomplish this. A WSDL file is another XML-based file that describes what a web service does with a client application. The client application will understand where the web service is located and how to access it using the WSDL document.
How does web service work?
The diagram shows a simplified version of how a web service would function. The client will use requests to send a sequence of web service calls to the server hosting the actual web service.
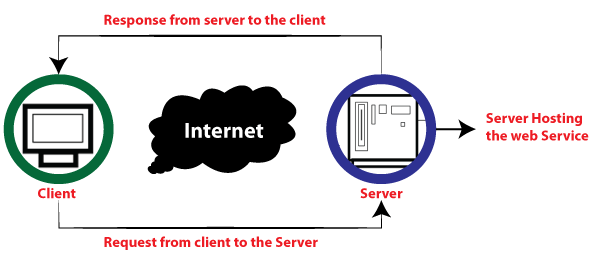
Remote procedure calls are used to perform these requests. The calls to the methods hosted by the respective web service are known as Remote Procedure Calls (RPC). Example: Flipkart provides a web service that displays the prices of items offered on Flipkart.com. The front end or presentation layer can be written in .NET or Java, but the web service can be communicated using a programming language.
The data exchanged between the client and the server, XML, is the most important part of web service design. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a simple, intermediate language understood by various programming languages. It is the equivalent of HTML.
As a result, when programs communicate with each other, they use XML. It forms a common platform for applications written in different programming languages to communicate with each other.
Web services employ SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) to transmit XML data between applications. The data is sent using standard HTTP. A SOAP message is data sent from a web service to an application. An XML document is all that is contained in a SOAP message. The client application that calls the web service can be built in any programming language as the content is written in XML.
Features of Web Service
Web services have the following characteristics:
(a) XML-based: A web service’s information representation and record transport layers employ XML. There is no need for networking, operating system, or platform bindings when using XML. At the mid-level, web offering-based applications are highly interactive.
(b) Loosely Coupled: The subscriber of an Internet service provider may not necessarily be directly connected to that service provider. The user interface for a web service provider may change over time without affecting the user’s ability to interact with the service provider. A strongly coupled system means that the decisions of the mentor and the server are inextricably linked, indicating that if one interface changes, the other must be updated.
A loosely connected architecture makes software systems more manageable and easier to integrate between different structures.
(c) Ability to be synchronous or asynchronous: Synchronicity refers to the client’s connection to the execution of the function. Asynchronous operations allow the client to initiate a task and continue with other tasks. The client is blocked, and the client must wait for the service to complete its operation before continuing in synchronous invocation.
Asynchronous clients get their results later, but synchronous clients get their effect immediately when the service is complete. The ability to enable loosely connected systems requires asynchronous capabilities.
(d) Coarse Grain: Object-oriented systems, such as Java, make their services available differently. At the corporate level, an operation is too great for a character technique to be useful. Building a Java application from the ground up requires the development of several granular strategies, which are then combined into a coarse grain provider that is consumed by the buyer or service.
Corporations should be coarse-grained, as should the interfaces they expose. Building web services is an easy way to define coarse-grained services that have access to substantial business enterprise logic.
(e) Supports remote procedural calls: Consumers can use XML-based protocols to call procedures, functions, and methods on remote objects that use web services. A web service must support the input and output framework of the remote system.
Enterprise-wide component development Over the years, JavaBeans (EJBs) and .NET components have become more prevalent in architectural and enterprise deployments. Several RPC techniques are used to both allocate and access them.
A web function can support RPC by providing its services, similar to a traditional role, or translating incoming invocations into an EJB or .NET component invocation.
(f) Supports document exchanges: One of the most attractive features of XML for communicating with data and complex entities.
