What is Privileged Access Management for Active Directory Domain Services in Azure?
A solution for limiting privileged access within an isolated Active Directory environment is known as MIM Privileged Access Management as it is abbreviated as PAM.
By the use of PAM, we can achieve two main objectives:
- We can regain control of a hacked Active Directory environment by setting up a separate bastion environment that is known to be immune to malicious attacks.
- Isolate privileged account usage to limit the chance of credentials being stolen.
Note: MIM PAM is designed for on-premises AD environments that are isolated. Azure AD PIM is a service in Azure AD that lets us manage, control, and monitor access to Azure AD, Azure, and other Microsoft Online Services including Microsoft 365 and Intune.
What issues does MIM PAM assist with?
Today, attackers have far too easy access to Domain Admin account credentials, and it’s far too difficult to detect these attacks after they’ve occurred. PAM’s purpose is to decrease the chances of malevolent people gaining access while enhancing our control and knowledge of the environment.
The use of PAM makes it more difficult for attackers to break into a network and gain access to privileged accounts. PAM adds security to privileged groups, allowing them to regulate access to a variety of domain-joined PCs and applications. More monitoring, visibility, and fine-grained controls are also included. PAM allows businesses to gain a better understanding of how administrative accounts are used in the workplace.
The MIM PAM
PAM is based on the notion of just-in-time administration, which refers to administering just enough (JEA). The JEA toolkit for Windows PowerShell defines a set of commands for executing privileged tasks. It’s a command execution endpoint where administrators can gain permission to run commands. In JEA, an administrator decides which users with which privileges are allowed to accomplish which tasks.
The rights expire after a set amount of time, making it impossible for a malevolent person to gain access. And similarly, it gets enabled when a user meets the required conditions.
There are mainly 4 steps for setting up the PAM in our environment.
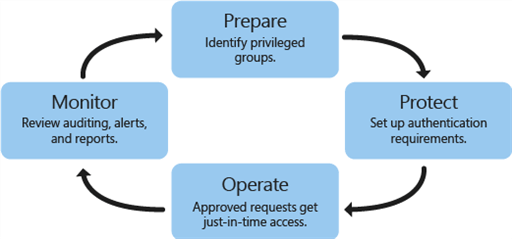
- Prepare: Determine which groups have important privileges in our current forest. In the bastion forest, recreate these groupings sans individuals.
- Protect: When users seek just-in-time management, set up lifecycle and authentication protection.
- Operate: A user account is temporarily added to a privileged group in the bastion forest when authentication requirements are completed and a request is authorized. The administrator has all powers and access permissions provided to that group for a predetermined period of time. The account is removed from the group after that period of time has passed.
- Monitor: PAM enhances privileged access requests with auditing, alarms, and reports. We may look up the history of privileged access and find out who did what. This phase is critical for detecting malicious software as well as tracing “inside” attackers.
What is MIM PAM and its working.
PAM is built on new AD DS features, especially for domain account authentication and authorization, as well as new Microsoft Identity Manager capabilities. PAM isolates privileged accounts from an Active Directory infrastructure already in place. A privileged account must first be sought and then approved before it may be utilized.
The MIM Service, Active Directory, and other components of this system can be implemented in a high-availability architecture as well.
The following example explains PIM in greater depth.
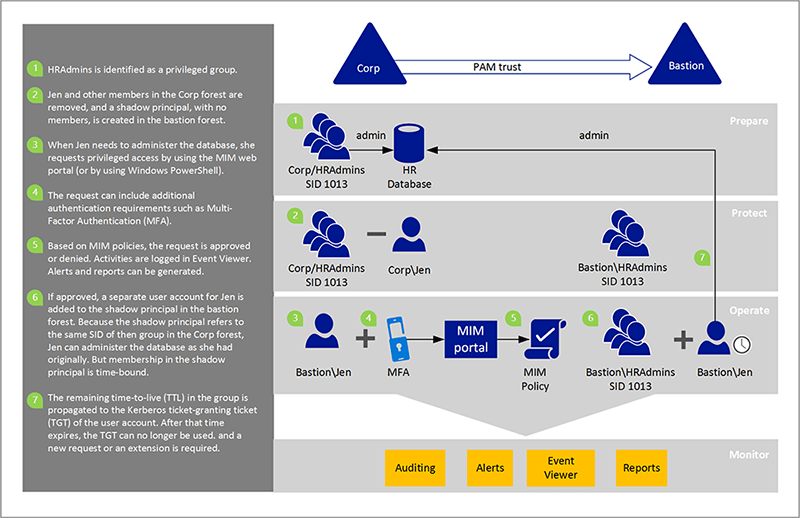
Time-limited group memberships are issued by the bastion forest, which in turn make time-limited ticket-granting tickets (TGTs).
User accounts that are used on a daily basis do not need to be moved to a new forest. The same may be said about computers, applications, and their associated organizations. They remain in an existing forest where they are now. Consider the case of a company that is concerned about cybersecurity today but does not have any immediate plans to upgrade its server infrastructure to the latest version of Windows Server. By combining MIM with a new bastion forest, that organization can still benefit from this integrated approach and better restrict access to current resources.
The advantages of PAM are as follows:
- Isolation/scoping of privileges: Privileges that are needed must be requested by users or else they will not be granted. MIM policies defined by a PAM administrator determine whether requests are allowed or rejected. Privilege access is not available until a request is authorized.
- Step-up and proof-up: The user can seek administrative account elevation, which is processed through MIM procedures.
- Customizable workflow: MIM workflows can be set up for a variety of circumstances, and several workflows can be employed depending on the specifications of the requesting user or requested responsibilities.
- Additional logging: PAM has additional logging that identifies the request, how it was permitted, and any events that occur after approval, in addition to the built-in MIM procedures.
What are the various processes and monitoring options?
Before the PAM was installed, let us suppose that the user was a member of an administrative group. As part of PAM setup, the user is then removed from the administrative group, and a policy is created in MIM. The policy states that if a user seeks administrative access, the request will be granted and the user will be given a separate account in the bastion forest’s privileged group.
PAM
Microsoft advises implementing this privileged access strategy to reduce our organization’s risk of high-impact and high-probability privileged access attacks.
Every organization’s top security priority should be privileged access. Any compromising of these users will very certainly have a severe negative impact on the company. When attackers get access to privileged users’ accounts, they almost always have a major impact on the organization’s business vital assets.
Microsoft has offered implementation guidelines to assist us in quickly deploying this strategy’s defences.
Important
There is no one technical solution that will miraculously limit the danger of privileged access; instead, we must combine numerous technologies into a holistic solution that defends against many attackers’ entry points. Organizations must bring the appropriate instruments for each task.
What is the significance of privileged access?
Because privileged access security is basic to all other security assurances, an attacker in possession of our privileged accounts can jeopardize all other security safeguards.
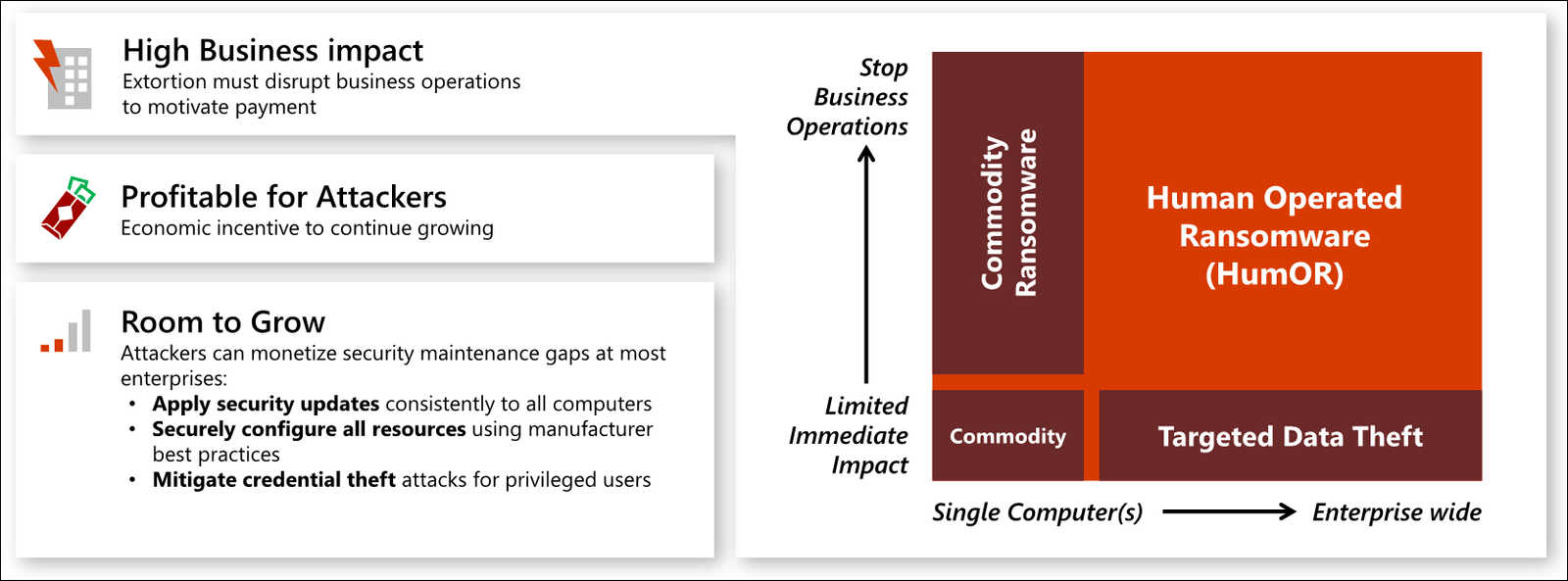
These attack approaches were first utilized in targeted data theft assaults, which resulted in a number of high-profile breaches at well-known companies (and many unreported incidents). More recently, ransomware attackers have embraced similar approaches, resulting in an explosion of highly profitable human-operated ransomware attacks that impair corporate operations across industries.
Important
Human-controlled ransomware is distinct from single-computer ransomware attacks that target a single computer or device.
This graph depicts how the impact and likelihood of this extortion-based assault employing privileged access is increasing:
- Significant economic impact
- It’s difficult to overestimate the business impact and damage that a loss of privileged access could cause. Attackers with privileged access effectively have complete control over all enterprise assets and resources, allowing them to reveal any secret information, halt all business processes, or corrupt business processes and machines to cause property damage, injury, or worse. Across every industry, there has been a massive business impact, including:
- Targeted data theft – Attackers exploit privileged access to get access to sensitive intellectual property and steal it for their own use or to sell or transfer it to competitors or foreign governments.
- Since the introduction of advanced credential theft methods, such as pass the hash techniques, the prevalence of privileged access attacks has increased.
These assaults were common prior to the introduction of human-operated ransomware (HumOR), but they were often ignored or misinterpreted due of:
- Attacker monetization limits & Silent Impact – These attacks could only benefit parties and individuals who knew how to commercialize sensitive intellectual property from target firms.
Both the silent impact and attacker monetization limitations on these attacks are disintegrating with the advent of human operated ransomware, which is growing in volume, impact, and awareness because it is both: - Loud and disruptive – from business operations to blackmail demands payment.
- Universally applicable – Every company in every field has a financial incentive to keep operating as usual.
For these reasons, any organization’s top security priority should be privileged access.
Holistic practical strategy
A comprehensive, holistic, and prioritized combination of risk mitigations spanning several technologies is required to reduce the risk of privileged access.
Building this strategy requires understanding that attackers are like water in that they have a plethora of options (some of which may appear small at first), are flexible in which ones they utilize, and generally pursue the path of least resistance to achieve their goals.
