Write Python Program to Search an Element in Sorted Array
In this tutorial, we will solve one of the interesting problems of the sorted array. But there is one twist; the given array may be rotated at the some index position. It means the few elements of the sorted array might be rotated at the given index. To understand it better, let’s understand the following problem statement.
Problem Statement –
An array is given as list1 sorted in the ascending order with the distinct values. It can be rotated at an unknown pivot index k (1 <= k < list1.length) such that the resulting array is [list1[k], list1[k+1], …, list1[n-1], list1[0], list1[1], …, list1[k-1]] (0-indexed).
Suppose the given array is [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] and it might be rotated at pivot index 3 and become [8, 9, 10, 11, 4, 5, 6, 7].
Given an array list1 after the possible rotation and an integer target, return the index of the target; if exist otherwise, return -1.
Example – 1:
Input: list1 = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], target = 0
Output: 4
Example – 2:
Input: list1 = [4, 5 ,6, 7, 0, 1, 2], target = 3Output: -1
Now we will find the best approach to solve this problem. It is a slightly tricky question, but we can easily write the code when we break down the solution. Let’s understand the following solution.
Solution
To the search related problems, we think to implement the binary search algorithm first because it is easy and quite efficient algorithm to search an element. However, the given list must be sorted, in our case the array is sorted but rotated at some place. Let’s see the following array.
list1 = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]
If we observe closely, we can see that the normal array will be [0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7], and it is rotated at the index of 3.
Now the array can see that the array is split into two parts, the left portion is sorted as [4, 5, 6, 7,] and the right portion is [0, 1, 2]
Let’s represents it using the graph to take an advantage of binary search algorithm for this problem.
We draw a basic graph that has the contiguously basic increasing line might not be necessary linear but always in increasing order.

Hence the new graph will be formed as below.
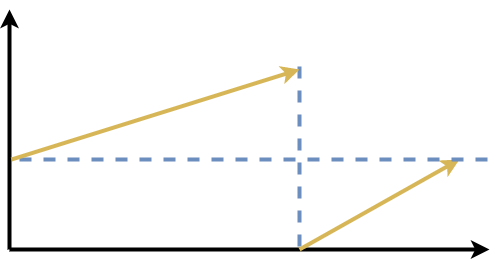
Now we can find a pattern that can help us write the solution. As we know that there are three-pointers in the binary search – left, right, and mid. There are two portions in the array, both independently sorted. As we know that there are three pointers in the binary search – left, right, and mid.
Suppose in the given array [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2] the target value is 0 and the mid is 6, it means if the target value is greater than 6, it won’t be exited on the left side.
Now we can search the element on the right side. What if the target value is less than the mid?
In that scenario, 4, 5 are less than 6 and 0, 1, 2 less than 6, so how do we know which side to be searched for?
So here check the leftmost value of the list, if it is less than the target value then we don’t need to search it at left side anymore.
The search will be placed at right side from mid + 1. But if the target value is greater than the leftmost value, we search the element at the left side.
Now consider the mid-value as 1; the only element is less than 1 is 0. So the search will happen on the left side. We check the leftmost value and compare it with the target value if it is greater than the rightmost value. Let’s implement it using Python code.
Note – To check whether the middle value belongs to the left portion or right, we can use compare with the leftmost value to mid. If the mid-value is greater than the leftmost value, it must be belonged to the left portion and vice-versa.
Python Code –
Output:
The element is at the 4 index
It might seem slightly complicated but once understand the concept. It will be clear.
Time Complexity
The time complexity will be O(logN) because binary search requires log n comparison to find the element. The space complexity will be O(1) because we don’t require the extra space.
