The Rabin-Karp-Algorithm
The Rabin-Karp string matching algorithm calculates a hash value for the pattern, as well as for each M-character subsequences of text to be compared. If the hash values are unequal, the algorithm will determine the hash value for next M-character sequence. If the hash values are equal, the algorithm will analyze the pattern and the M-character sequence. In this way, there is only one comparison per text subsequence, and character matching is only required when the hash values match.
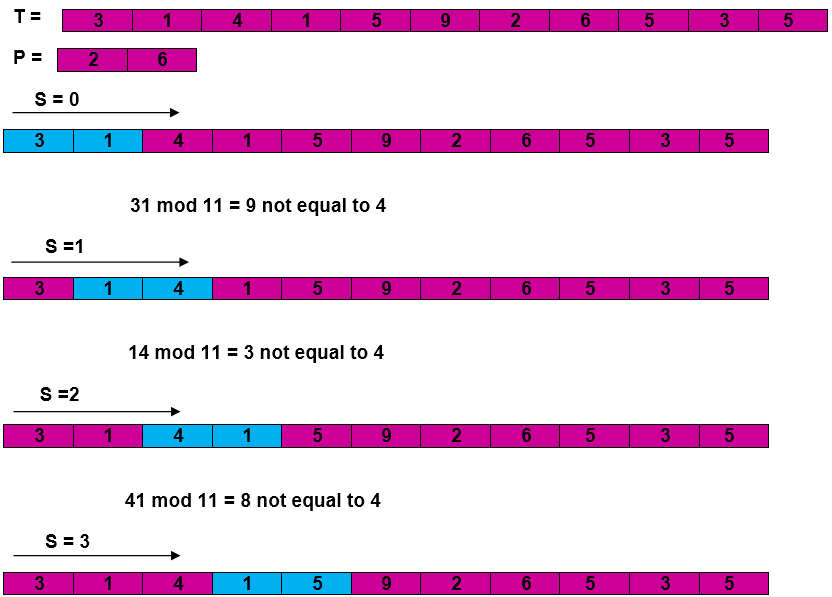
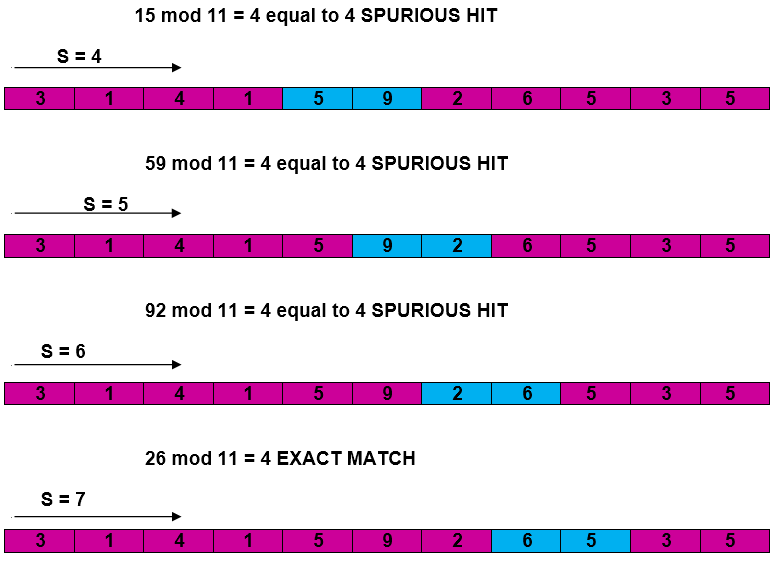
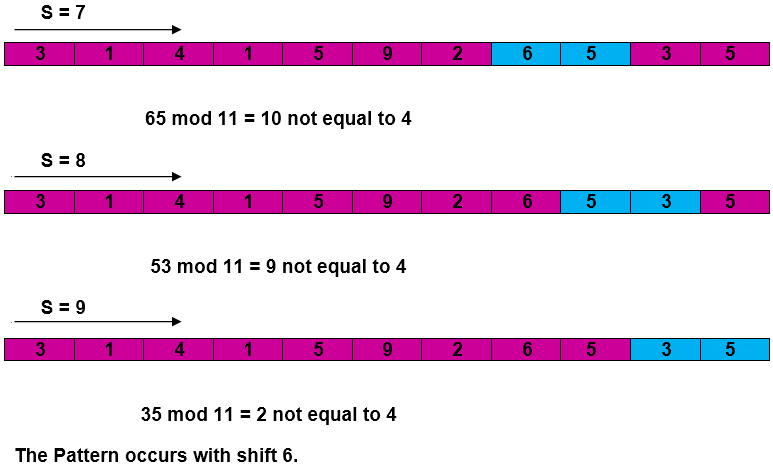
RABIN-KARP-MATCHER (T, P, d, q) 1. n ← length [T] 2. m ← length [P] 3. h ← dm-1 mod q 4. p ← 0 5. t0 ← 0 6. for i ← 1 to m 7. do p ← (dp + P[i]) mod q 8. t0 ← (dt0+T [i]) mod q 9. for s ← 0 to n-m 10. do if p = ts 11. then if P [1.....m] = T [s+1.....s + m] 12. then "Pattern occurs with shift" s 13. If s < n-m 14. then ts+1 ← (d (ts-T [s+1]h)+T [s+m+1])mod q
Example: For string matching, working module q = 11, how many spurious hits does the Rabin-Karp matcher encounters in Text T = 31415926535…….
Solution:
Complexity:
The running time of RABIN-KARP-MATCHER in the worst case scenario O ((n-m+1) m but it has a good average case running time. If the expected number of strong shifts is small O (1) and prime q is chosen to be quite large, then the Rabin-Karp algorithm can be expected to run in time O (n+m) plus the time to require to process spurious hits.