Digital Communication MCQs
1) What are the primary features of a transmitter?
- Lower clock speed
- Lower transmitting power
- Higher clock speed
- None of these
Answer: d
Explanation: A transmitter refers to an electronic device that produces a radio signal with the help of an antenna. The primary features which make a transmitter complex are higher transmitting power, higher clock speed, directional antennas.
2) The window gives a number of
- Bytes
- Frames
- Both option a and b
- None of these
Answer: c
Explanation: The window gives the number of frames or bytes.
3) A speech signal, band-limited to 8 kHz with peak to peak between +20 V to – 20 V, and the signal are sampled at Nyquist rate, and the bits 0 and 1 are transmitted using bipolar pulses. Find the minimum bandwidth for distortion-free transmission in KHz?
- 98
- kHz
- 64 kHz
- 52 kHz
- 35 kHz
Answer: b
Explanation:
While using polar pulses, the minimum bandwidth required is four times the theoretical bandwidth or Nyquist bandwidth.
So the required bandwidth = 4 * Nyquist bandwidth
= 4 × 2 FM = 4 × 2 × 8 = 64 KHz.
4) Which of the given device does the data compression?
- Switches
- Circuit breakers
- Microcontroller
- Source encoder
Answer: d
Explanation: Data compression refers to a reduction in the number of bits required to present the data. The compressing data can save memory, increase the file transfer rate, and minimize the cost for storage hardware and network bandwidth. Source encoder is a type of encoder which converts the digital signal or analog signal to a binary digit sequence.
5) According to Federal communications commission regulations, the maximum allowable frequency deviation is 40 kHz, for a TV signal, given that the percentage modulation of the audio portion is 50%. Find the frequency deviation of the audio signal in KHz?
- 10
- kHz
- 20 kHz
- 30 kHz
- 40 kHz
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
Maximum allowable frequency deviation ?fmax = 40 KHz
Percentage modulation of the audio portion = 50%
We know that the actual frequency deviation for the TV signal is calculated as
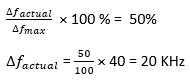
6) Which of the given filter has maximum flatness?
- Bessel filter
- Butterworth filter
- Low pass filter
- None of these
Answer: b
Explanation: Butterworth filter refers to a type of filter whose frequency response is flat over the passband region. The low pass filter provides a constant output source from DC up to a cutoff frequency. If the signal is beyond the cutoff frequency, it simply rejects.
7) For an Amplitude modulation signal, the bandwidth is 20 kHz, and the highest frequency component present is 650 kHz. Find the carrier frequency used for this amplitude modulation signal?
- 640
- kHz
- 900 kHz
- 440 kHz
- 260 kHz
Answer: a
Explanation:
Given;
Bandwidth = 20 KHz
FC + FM = 650 KHz
We know that,
BW = 2 FM = 20 KHz
So, fm = 10 KHz
Therefore,
FC = 650 kHz – FM
FC = 650 – 10 = 640 KHz
8) Space loss occurs due to a decrease in
- Phase shift
- Momentum
- Electric field strength
- Power
Answer: c
Explanation: Space loss occurs mainly due to a decrease in electric field strength. Due to a decrease in the electric field strength, there will be a reduction in the signal strength as a function of distance known as space loss.
9) Analog data with the highest harmonic at 40 kHz generated by a sensor has been digitized using 6 level PCM. Find the rate at which digital signal generated?
- 300 kbps
- 240 kbps
- 450 kbps
- 600 kbps
Answer: b
Explanation:
We know that,
Nyquist rate = 2 × 40 kHz = 80 KHz
2n ≥ 6
Thus, n = 3
So the bit rate = 80 × 3 = 240 kbps
10) A satellite receiver with a noise figure of 5.6 dB has a bandwidth of 24 kHz and comprises a preamplifier with a noise temperature 150 k and a gain of 40 dB. If the reference temperature is 300 k, find the equivalent noise temperature of the receiver?
- 450 K
- 300 K
- 220 K
- 150 K
Answer: d
Explanation:
Given;
F2 = 5.6 dB = 3.63
Teq = 150
T = 300
We know that,
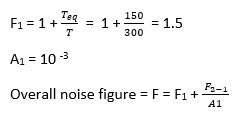
= 1.5 + ( 2.63 × 10 -3 ) = 1.50
Therefore, the equivalent noise temprature
Te = (F – 1) T = (1.50 – 1) 300 = 150 K
11) In frequency modulation broadcast, the maximum deviation is 80 kHz, and the maximum modulating frequency is 20 kHz. In reference to Carson’s rule, find the maximum required bandwidth?
- 300 KHz
- 200 KHz
- 150 KHz
- 80 KHz
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
Maximum deviation = 80 KHz
Maximum modulating frequency = 20 KHz
We know that,
According to Carson’s rule,
BW = 2 (fm + ?f) = 2 (20 + 80) = 200 KHz
12) If noise figure of a receiver is 1.8 at 20 oC, find its equivalent noise temprature?
- 474.9 K
- 384.8 K
- 234.4 K
- 184.6 K
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
Noise figure of a recevier (NF) = 1.8
TO = 273 + 20 = 293 K
We know that,
Equivalent noise temprature Teq = TO( NF – 1)
= 293 (1.8 – 1 ) = 234.4 K
13) If a 120 V carrier peak changes from 170 V to 50 V by a modulating signal, find the modulation factor?
- 0.5
- 1.5
- 2.5
- 3.5
Answer: a
Explanation:
:
Modulation factor also refers in terms of the values referred to the modulated carrier wave and is given as
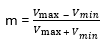
Where,
Vmax ? = Maximum values of the amplitude of the modulated carrier wave.
Vmin ? = Minimum values of the amplitude of the modulated carrier wave.
Therefore,
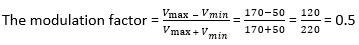
14) RF carrier 15 kV at 1 MHz is amplitude modulated and modulation index is 0.8. Find the peak voltage of the signal?
- 18 kV
- 22 kV
- 26 kV
- 12 kV
Answer: d
Explanation:
Given;
Modulation index (m)= 0.8
RF carrier = 15 kV
We know that,
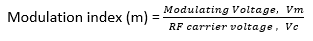
Therefore the peak value of signal Vm = m × amplitude of carrier wave, Vc
= 0.8 × 15 kV
= 12 kV
15) A broadcast amplitude modulation radio transmitter radiates 140 kW when the modulation percentage is 75. Find the carrier power?
- 120 kW
- 142 kW
- 109 kW
- 172 kW
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
Transmitted power Ptotal = 140 kW
Modulation percentage = 75 = 0.75
We know that,
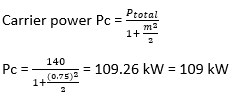
16) The power spectral density of a signal is
- Even negative and complex
- Odd, complex, and positive
- Real, odd, and negative
- Real, even, and non-negative
Answer: d
Explanation: We know that the power of a signal is real and non-negative quantity; therefore, the power spectral density of a signal is real, even, and non-negative quantity.
17) A 1200 W carrier is amplitude modulated and has a sideband power of 400 W. Find the depth of the modulation?
- 1.245
- 0.775
- 3.689
- 1.059
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
Pc = 1200 W
Psb = 400 W
We know that, power in sidebands is given as
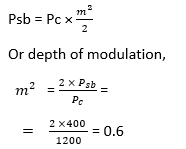
Or, m = √0.6 = 0.7746 = 0.775
18) A modulater is a device used to
- Differenciates two frequencies
- Amplify two radio frequency signal
- Impress the information on to a radio frequency carrier
- Reduce the modulating power requirement.
Answer: d
Explanation: Modulation refers to a low-frequency signal process combined with a high-frequency signal to transmit it over a long distance. For example, the normal human voice signal constitutes low frequency to travel only to a short distance. Hence, to transfer it to a long-distance, usually, we need modulation. In other words, we can say that it is a device used to impress the information present in low-frequency signals onto a radio frequency carrier.
19) If the two signals modulate the same carrier with different modulation depths of 0.4 and 0.8. Find the resulting modulation signal?
- 0.89
- 0.66
- 0.54
- 0.16
Answer: a
Explanation:
Given;
Two different modulation depths m1 = 0.4 and m2 = 0.8
We know that,
The total modulation index (depth)
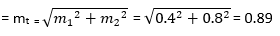
20) A balanced modulator is used in the generation of which of the following signal?
- Frequency Modulation signal
- DSB- SC signal
- ISI signal
- SSB -SC signal
Answer: b
Explanation: A balanced modulator can be defined as a circuit in which two non-linear devices are linked in a balanced mode to generate a DSB-SC signal.
21) A given AM broadcast station transmits an average carrier power output of 50kW and uses a modulation index of 0.804 for sign wave modulation. Find the maximum amplitude of the output if a 60 ohm resistive load represents the antenna?
- 5.88 kV
- 7.66 kV
- 3.95 kV
- 1.05 kV
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
Average carrier power output (Pc) = 50kW
Modualtion index (m)= 0.804
Resistive load (R) = 60 ohm
We know that,
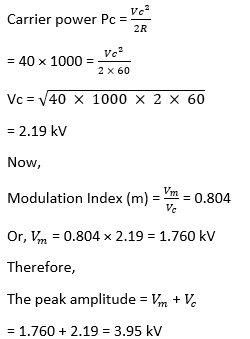
22) Which of the given modulator is an indirect way of generating FM?
- Inductance FET modulator
- Armstrong modulator
- Reactance tube modulator
- Zener diode modulator
Answer: b
Explanation: If we are talking about the direct method of FM generation, the VCO output frequency is controlled by the instantaneous value of the baseband signal. Reactance tube modulator facilitates it. In Armstrong modulation, FM is determined from PM, so it is an indirect method.
23) In a frequency modulation system, the maximum frequency deviation is 2000, and modulating frequency is 2kHz. Find the modulation index ??
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: a
Explanation:
Given;
?f = 2000
fm = 2 kHz = 2000 Hz
We know that,
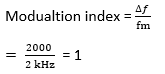
24) The maximum deviation allowed in a frequency modulation system is 120 kHz. If the modulating signal frequency is 20 kHz, find the bandwidth requirement as per Carson’s rule?
- 120 kHz
- 240 kHz
- 280 kHz
- 320 kHz
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
?f = 120 kHz
fm = 20 kHz
We know that,
The bandwidth requirement as per Carson’s rule
= 2 (1 + δ) fm
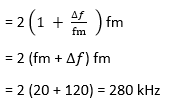
25) In FM modulation, when the modulation index increases, the transmitted power?
- Half
- Decreased
- Doubled
- Unchanged
Answer: d
Explanation: Frequency modulation refers to the process of modulating a sinusoidal wave frequency as per the amplitude of the baseband bearing signal. The signal can be digital or analog; in frequency modulation, the FM wave’s amplitude is always constant, and transmitted power Pt is equaled to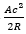
26) In a frequency modulated system, when the audio frequency is 600 Hz, and audio frequency voltage is 2.8 V, the frequency deviation ? is 5.6 kHz. If the audio frequency voltage is now increased to 7.4 V, find the new value of deviation?
- 12. 7 kHz
- 14. 8 kHz
- 15. 2kHz
- 17. 6 kHz
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
Modulation frequency , FM = 600 Hz
Audio frequency voltage Am= 2.8 V
Frequency deviation ?f = 5.6 kHz
We know that,
?f= Kf× Am
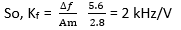
When amplitude of message signal is increased to 7.4 V
That is, A’m = 7.4 V
So, new frequency deviation,
?f’= Kf × A’m = 2 × 7.4 = 14. 8 kHz
27) In phase modulation, phase deviation is proportional to which of the following.
- The wavelength of the message signal
- Message signal
- The amplitude of the message signal
- The phase shift of the message signal
Answer: b
Explanation: In phase modulation, Phase deviation varies linearly with the message signal frequency so that phase deviation is proportional to the message signal.
28) A system has a receiver noise resistance of 60 ohms, and it is connected to an antenna with an output resistance of 60 ohms. Find the noise figure of the system?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given,
Req = 60 ohm
Ra = 60 ohm
We know that,
The noise figure is given as
NF = 1 + Req/Ra = 1 + 1/1 = 2
29) Which type of noise reduction by limiters in FM receivers
- Jhonson noise
- Cosmic noise
- Impulse noise
- Partition noise
Answer: c
Explanation: Under the ordinary condition, limiters in FM receivers limit the impulse noise to the same extent as the random noise.
30) When a radio receiver is tuned to 600 kHz, its local oscillator provides the mixer with input at 1000 kHz. Find the frequency of other stations?
- 1400 kHz
- 1600 kHz
- 1800 kHz
- 2200 kHz
Answer: a
Explanation:
Given;
Turned frequency, FC = 600 kHz
Local oscillator frequency, f = 1000
We know that,2
Local oscillator frequency, f = FC + fif
fif = f – FC
= 1000 – 600 = 400 kHz
Therefore, the image is given as
fc + 2 fif
= 600 + 2 × 400
= 600 + 800
= 1400 kHz
31) What is the automatic frequency control voltage of the FM transmitter VCO?
- Ac voltage
- Dc voltage
- Ramp voltage
- Sine wave voltage.
Answer: b
Explanation: VCO stands for the voltage-controlled oscillator. An oscillator refers to a circuit that producers an AC signal, usually of high frequency. A voltage-controlled oscillator is an oscillator whose frequency is controlled by voltage. It ranges from 1 MHz with one-volt input to 1 MHz per volt to 10v/10MHz.
32) Without any filtering, a broadcast station at 1.800 kHz is heard together with another station at 2800 kHz on a superheterodyne receiver. Find the value of employed IF?
- 200 kHz
- 400 kHz
- 500 kHz
- 600 kHz
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given
Image frequency = 2800 kHz
Signal frequency, fs = 1800 kHz
We know that the IF (Intermediate frequency),

33) If the turn-on energy loss in a transformer is 55 MJ and turn-off energy loss is 78 mj. If the mean power loss is limited to 220 W, find the maximum switching rate that can be achieved?
- 1232.7 cycles/s
- 1654.1 cycles/s
- 1453.8 cycles/s
- 1862.9 cycles/s
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
P = 220 W
We know that,
Energy loss = Mean power loss, P × time duration
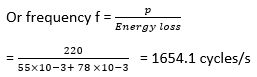
34) Analog data having the highest harmonic at 40 kHz generated by a sensor has been digitized using 6 level PCM; find the generated digital signal rate?
- 120 kbps
- 160 kbps
- 180 kbps
- 240 kbps
Answer: d
Explanation:
Given
L = 6
FM = 40 kHz
Since the number of quantization levels,
L = 2n
Therefore, L= 6 , 2n = 6 or n = 3
So 3 bits are required to represent each sample,
So the rate of a digital signal generated is given as
Rb = n × 2 × FM = 3 × 2 × FM = 3 × 2 × 40 = 240 kbps
35) In a delta modulation scheme, the step height is 80 mV, and the step width is 2 ms. Find the maximum slope that the staircase can track?
- 50 V
- 60 V
- 40 V
- 30 V
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
Step height = 80 Mv
Step width = 2 ms
We know that,
The maximum slope that the staircase can track in a delta modulation scheme is given as
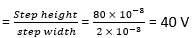
36) Frequency frogging is used in carrier system to
- Reduce frequencies
- Reduce cross-talk
- Reduce error rate
- Conserve narrowband signals.
Answer: b
Explanation: Frequency frogging means the interchanging of frequencies. It performs specific tasks such as avoiding oscillations and feedback to reduce cross-talk and correct for a high-frequency response slope in the transmitter line.
37) A TDM link has 25 signal channels, and each channel is sampled at 7 kHz. If each sample is represented by 8 bits and contains an additional bit for synchronization, find the total bit rate for the TDM link?
- 695 kbps
- 888 kbps
- 1407 kbps
- 1209 kbps
Answer: c
Explanation:
Given;
Number of channel N = 25
Sampling frequency, fs = 7 kHz
Number of bits, n = 8
Additional bit C = 1 (Smaplw contains one additional bit)
Bit rate, Rb = N × n × fs + Cfs
= 25 × 8 × 7 + 1 × 7
= 1407 kbps
38) Output data ratio of a 4 bit PCM – TDM system sampling 16 voice channels, comparing these using µ – law at the rate of 6 kHz and with an Iframe alignment word, is
- 6.04 × 104bit/sec
- 4.08 × 103bit/sec
- 8.03 × 102bit/sec
- 5.97 × 105bit/sec
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
n =4
N = 16
a = 1
Fs = 6 × 103
We know that,
Each frame alignment consists of a synchronizing bit in addition to data, so the equation is given as
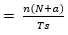
As we know, Ts = 1/fs, therefore
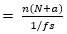
= n (N + a) × fs
= 4 (16 + 1) × 6 × 103
= 4.08 × 103bit/sec
39) 23 voice channels are sampled uniformly at a rate of 10 kHz and then time division multiplexed. The sampling process uses flat-top samples with a two µs duration. The multiplexing operation includes the provision of synchronization by adding an extra pulse of 2 µs duration. Find the spacing between successive pulses of the multiplexed signal?
- One µs
- Two µs
- Three µs
- Four µs
Answer: b
Explanation:
Given;
Number of voice signals = 23
Synchronization pulses = 2
Total number of pulses in one rotation = 23 + 2 = 25
We knonw that,
The time duration for one time frame,
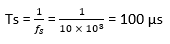
So time duration utilized by 25 pulses = 100 µs
Therefore, the time utilised by each pulse
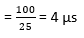
Since actual duration of each pulse is 2 µs
So, the spacing between successive pulse = 4 – 2 = 2 µs
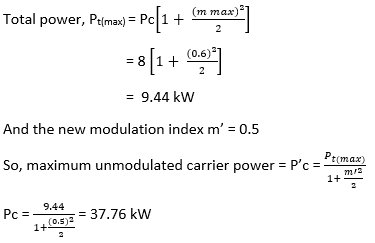
40) The unmodulated carrier power in an AM transmitter is 8 kW. A sinusoidal modulating signal modulates this carrier. The maximum percentage of modulation is 60 %. If it is reduced to 50 %, find the maximum unmounted carrier power in (kW) that can be used without overloading the transmitter?
- 37.76 kW
- 25.34 kW
- 18.55 kW
- 42.57 kW
Answer: a
Explanation:
Unmodualted carrier power Pc = 8 kW
Maximum modulation index mmax = 0.6
We know that, total power is given as
41) For an Amplitude modulation signal, the bandwidth is 10 kHz, and the highest frequency component present is 450 kHz. Find the carrier frequency used for this amplitude modulation signal?
- 50 KHz
- 930 KHz
- 440 KHz
- 280 KHz
Answer: a
Explanation:
Given;
Bandwidth = 10 KHz
fc + fm = 450 KHz
We know that,
BW = 2 fm = 10 KHz
So, fm = 5 KHz
Therefore,
fc = 50 KHz – fm
fc = 450 – 10 = 440 KHz
