List of Banks in India
What is Bank?
A bank is a type of financial institution that allows the public to deposit and borrow money. The functions of banks are governed by legislation. Different countries have different laws for the establishment and working of a bank. People who work at a bank are known as bank employees. Certain banks deal directly with the public, while other banks handle investments and international currency trading.
The word bank is derived from the Italian word banca, which means a bench or a counter.
A bank is not only a safe place to deposit money but also a reliable place to take loans that are repaid to the bank with interest later. For example, obtaining a mortgage to purchase a home or apartment. Banks can also invest the money they have from deposit accounts in businesses to increase their profits.
In most nations, the government sets the rules for banks through legislation. The amount of money released at any time is adjusted by a central bank (such as the Bank of England). It is a determinant in a country’s economy, and the government is in charge of major choices.
The Indian Banking System
Banking was initially introduced to India in the first part of the 18th century. The General Bank of India, which is created in 1786, was the country’s first bank. The State Bank of India, originally known as The Bank of Bengal, was founded in Kolkata in 1806. The Reserve Bank of India supervises all banks in India. All Indian banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India or RBI. In 1935, this governing body had the responsibility of formally regulating Indian banks. The Reserve Bank of India has been designated as the country’s official Central Banking Authority, overseeing the country’s banking sector. In India, there are two sorts of banks: public sector banks and private sector banks.
A bank often offers the following services:
- Checking account
- Cheque books
- Savings account
- Money market account
- Certificate of deposit (CD)
- Individual retirement account (IRA)
- Credit card
- Debit card
- Mortgage
- Individual loan
- Automated teller machine
- Transactional account
Furthermore, banking sector offers a variety of services such as personal banking, corporate banking, investment banking, private banking, transaction banking, insurance, consumer lending, trade finance, and other related services.
In India, banks are categorized into four types:
A strong banking system is critical because it assures public wealth, access to low-cost loans, economic growth, rural development, and worldwide reach. India has a large number of banks that are categorized into numerous types. But the best part is that they are all RBI-licensed, which means they are safe and reliable. The four types of banks in India are as follows;
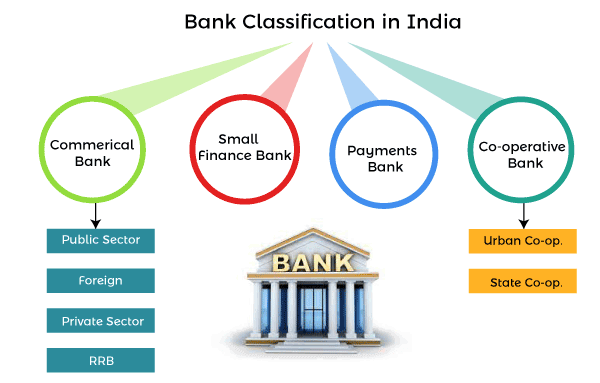
- Bank for business (Commercial bank)
- Small finance Institutions/Bank
- Banks that accept payments (Payments Bank)
- Banks that operate together (Co-operative Bank)
Brief Explanation about these four banks:
1. Commercial bank: A commercial bank is a financial institution that accepts public deposits and lends money for profitable consumption and investment. Also, a large bank’s section that interacts with companies or large/middle-sized organizations might be referred to as a corporate bank to distinguish it from retail banking and investment banking. Commercial banks are divided into two types: private sector banks and public sector banks.
Primary functions
- Commercial banks accept numerous public deposit types from their clients and the general public, including savings account deposits, recurring account deposits, and fixed deposit types. These deposits are repaid when the customer requests them or after a set length of time.
- Commercial banks offer various loans and advances, such as overdrafts, cash credit, bill discounting, money at call, and so on. They also provide demand and term loans to a wide range of consumers in exchange for adequate collateral. They also serve as trustees for their customers’ wills and other assets.
- The credit creation function is generated based on a credit and payment intermediary. To convert loans into derivative deposits, check circulation and transfer settlement are employed. To some extent, the derivative funds are grown many times the original deposits, which considerably increases the driving force of commercial banks to service economic development.
i) Public sector banking
The banking activities of a specific type of commercial bank are referred to as public sector banking. The exact meaning of this statement varies depending on the country or region of the world in which it is used. Public-sector banks are those owned or operated by national governments in general. Some countries use this sort of banking more than others, but “public sector banking” is common in many regions where state control is still prevalent.
ii) Private sector banking- Private sector banks are ones in which private individuals or private corporations possess a significant portion of the bank’s equity. A big portion of these banks’ shares are traded on the stock market, and anyone can purchase a significant portion of these banks’ shares on the stock market. Even while these banks adhere to the standards of the country’s central bank, they are free to develop their financial strategies for their consumers. Private sector banks in India fall into two categories: old and modern.
- Before nationalization in 1969, old private sector banks maintained their independence because they were either too tiny or too specialized to be included.
- Following the deregulation of the 1990s, the new private sector banks gained a banking license.
2. Small Finance Bank: Small finance banks are a type of specialist bank in India. Banks with a small finance bank license can offer basic banking services such as deposit acceptance and lending. Tiny business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small firms, and unorganized sector organizations are among the areas of the economy that other banks do not currently handle.
Objectives of small finance bank:
The objectives of setting up small finance banks will be to improve financial inclusion by:
i) Providing savings vehicles primarily to unserved and underserved segments of the population, and promoting financial inclusion in general.
ii) Financing to small business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries, and other unorganized sector organizations via high-tech, low-cost operations.
3. Payments banks: A payments bank is comparable to any other bank, except that it operates on a smaller scale and does not take on any credit risk. In other words, it can perform the majority of banking functions but cannot make loans or issue credit cards. It can accept demand deposits of up to Rs 1 lakh, remittances, mobile payments/transfers/purchases, and other banking services such as ATM/debit cards, net banking, and third-party cash transfers.
4. Cooperative Banks: Cooperative Banks are a type of bank that is owned and operated by its members. The term “cooperative” comes from the Latin word “cooperat” or “cooperate,” which means “worked together.” It means that people band together and help each other out since they have similar interests. Similarly, cooperative banks are associations of people who have a shared belief and get together to collaborate. A cooperative bank is one of the financial entities that belong to its members, who are also the bank’s owners and clients. Cooperative banks are further classified into two types:
i) State Cooperative Banks: A state cooperative bank is a federation of the cooperative central bank that serves as the custodian of the cooperative banking structure in the state. Its funds are derived from the Reserve Bank of India’s social capital, deposits, loans, and overdrafts. State-owned cooperative banks provide money to cooperative central banks and primary companies rather than to farmers directly.
ii) Urban Co-operative Bank: Although not formally defined, the term Urban Co-operative Banks (UCB) refers to primary cooperative banks in urban and semi-urban areas. Until 1996, these banks could only lend money for non-agricultural uses. This distinction is no longer met nowadays. Traditionally, these banks concentrated on communities, towns, and workplace organizations. They mostly lend to small borrowers and enterprises. Its operating environment has grown significantly in recent years.
The Goal of Cooperative Banks
- The primary goal of cooperative banks is to provide low-cost financial services based on mutual assistance. It benefits persons with limited resources or those who are not financially secure. It also encourages the practice of economy, saving, and mutual assistance.
- Earning profit is not taboo; nonetheless, the motive must be non-profit; the motive cannot be profit-earning; yet, there is no prohibition on profiting from the activities and amenities given by cooperative banks to its customers.
Other Bank types:
i) Foreign bank: Foreign banks have their origins in another country and provide services to people in that country. In simple terms, foreign banks in India are banks whose headquarters are located in another nation but whose functions are managed from India. It must also adhere to the norms and obligations of both the Host and Parent countries.
Foreign banks’ functions
Foreign banks are not often from the host country, but as previously stated, they must adhere to the host country’s legislation. If an international bank wishes to begin operations, it may do so in any of two ways.
- Foreign banks operating in India may open its branch.
- Foreign banks in India may also have a presence in the form of a representative office.
ii) Rural Regional Bank
After the nationalization of banks in India in 1969, the banking system began to improve. Our Indian government owns RRB-Regional Rural Bank, a commercial bank. Regional Rural Bank has contributed to the growth of our Indian economy. The Regional Rural Bank was established to help India’s rural areas thrive.
Functions of Regional Rural Banks:
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are local-level banking operations in all Indian states. They were established to provide basic banking and financial services, particularly to the country’s rural areas. On the other hand, Regional Rural Bank may have branches established up for urban operations, and their service area may also encompass metropolitan regions.
The objectives of Regional Rural Banks.
- Providing banking services to rural and semi-urban areas is the major objective of Regional Rural Banks.
- Distribution of pensions, carrying out government procedures such as payment of MGNREGA workers’ wages, etc.
- Providing non-banking services such as lockers, debit, and credit cards.
- To protect impoverished rural people from moneylenders.
- To expand job prospects in rural areas by fostering trade and commerce.
- To promote entrepreneurship in rural communities.
So, here is the list of Banks in India. It will assist you in gaining an understanding of their performance and dependability.
List of all public sector banks in India
| Bank Name | Headquarter | Number of branches | Number of ATMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| State bank of India (SBI) | Mumbai | 24000 | 58599 |
| Bank of Baroda | Vadodara | 8581 | 10318 |
| Canara bank | Bengaluru | 10391 | 12829 |
| Union bank of India | Mumbai | 9500 | 13300 |
| Bank of India | Mumbai | 5825 | 5000 |
| Indian bank | Chennai | 6000+ | 6104 |
| Central bank of India | Mumbai | 2876 | 4666 |
| UCO bank | Chennai | 2377 | 4000 |
| Punjab and Sindh bank | New Delhi | 10451 | 1554 |
| Indian overseas bank | Chennai | 2995 | 3400 |
| Bank of Maharashtra | Pune | 1860 | 1897 |
| Punjab national bank | New Delhi | 11437 | 8985 |
List of private sector banks in India
| Bank Name | Headquarter | Number of branches | Number of ATMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 1050 | 1305 |
| South Indian bank | Thrissur, Kerala | 852 | 1393 |
| RBL bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 342 | _ |
| Lakshmi Vilas bank | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | 570 | 1045 |
| Karnataka bank | Mangaluru, Karnataka | 8351 | 1503 |
| Jammu Kashmir bank | Srinagar, Jammu Kashmir | 952 | 1322 |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 1369 | 2429 |
| National bank | Nainital, Uttarakhand | 135 | _ |
| Tamilnad mercantile bank limited | Thoothukudi Tamil Nadu | 5091 | 1156 |
| Kaur Vysya bank | Kaur Tamil Nadu | 668 | 1641 |
| Axis bank | Mumbai | 4094 | 17315 |
| Bandhan bank | Kolkata, West Bengal | 1000 | 485 |
| DCB bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 332 | 499 |
| Federal bank | Alva, Kerala | 1252 | 1598 |
| HDFC Bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 4787 | 13514 |
| IDBI bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 1892 | 3693 |
| City union bank | Thanjavur Tamil Nadu | 600 | 1724 |
| ICCI Bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 48821 | 5159 |
| Dhan Laxmi bank | Thrissur Kerala | 269 | 469 |
| IndusInd bank | Mumbai, Maharashtra | 1004 | 2662 |
List of regional rural banks in India
| S.NO. | Regional Rural Bank Name | State |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tamil Nadu Grama Bank | Tamil Nadu |
| 2. | Tripura Bank | Tripura |
| 3. | Utkal Grameen bank | Odisha |
| 4. | Uttarakhand Grameen Bank | Uttarakhand |
| 5. | Punjab Grameen Bank | Punjab |
| 6. | Mizoram Rural Bank | Mizoram |
| 7. | Nagaland Rural Bank | Nagaland |
| 8. | Manipur Rural Bank | Manipur |
| 9. | Kerala Grameen Bank | Kerala |
| 10. | Karnataka Grameen Bank | Karnataka |
| 11. | Baroda UP Bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 12. | Baroda Gujrat Grameen Bank | Gujrat |
| 13. | Baroda UP bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 14. | Aryavart Bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 15. | Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 16. | Himachal Pradesh Grameen Bank | Himachal Pradesh |
| 17. | J & k Grameen Bank | Jammu Kashmir |
| 18. | Madhya Pradesh Grameen Bank | Madhya Pradesh |
| 19. | Prathama UP Grameen Bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 20. | Punjab Grameen Bank | Punjab |
| 21. | Uttar Bihar Grameen Bank | Bihar |
| 22. | Telangana Grameen Bank | Telangana |
| 23. | Utkal Bengal kshatriya Grameen Bank | West Bengal |
| 24. | Saurashtra Grameen Bank | Gujrat |
| 25. | Sarva Haryana Grameen Bank | Haryana |
List of foreign banks in India
| S.No. | Foreign bank name |
|---|---|
| 1 | AB bank |
| 2 | American Express |
| 3 | Australia and New Zealand Banking Group |
| 4 | Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank |
| 5 | Bank of America |
| 6 | Bank of China |
| 7 | Bank of cyclone |
| 8 | Bank of nova scotia |
| 9 | Barclays bank PLC |
| 10 | BNP Paribas |
| 11 | CTBC bank |
| 12 | City Bank India |
| 13 | Credit Suisse |
| 14 | Rabobank |
| 15 | Sberbank s |
| 16 | Sonali Bank |
| 17 | United overseas bank |
| 18 | MUFG Bank |
| 19 | Standard chartered bank |
| 20 | State bank of Mauritius |
| 21 | Qatar National bank |
| 22 | Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation |
| 23 | Industrial bank of Korea |
| 24 | Industrial and commercial bank of China |
| 25 | HSBC bank |
| 26 | Westpac banking corporation |
| 27 | Bank of Bahrain and Kuwait |
| 28 | Woori bank |
| 29 | First rand bank |
| 30 | Emirates NBD |
List of small finance banks in India
| Small finance bank name | Headquarters | Established | Branches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ujjain small finance bank | Bangalore, Karnataka | 2017 | 464 |
| Jana small finance bank | Bangalore, Karnataka | 2018 | _ |
| Equites small finance bank | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | 2016 | 412 |
| AU Small finance bank | Jaipur, Rajasthan | 2017 | 396 |
| Capital small finance bank | Jalandhar, Punjab | 2016 | _ |
| North east small finance bank | Guwahati, Assam | 2017 | _ |
| ESAF small finance bank | Thrissur, Kerala | 2017 | _ |
| Fincare small finance bank | Bangalore, Karnataka | 2017 | 400 |
| Sarvodaya Finance bank | Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra | 2017 | _ |
| Utkarsh Finance bank | Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh | 2017 | _ |
List of payment banks in India
| List of small finance in India | Headquarters | Established | Branches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fino Payments Bank | Mumbai,Maharashtra | 2017 | 410 |
| Jio Payments bank | Mumbai,Maharashtra | 2017 | _ |
| Paytm Payments Bank | Noida, Uttar Pradesh | 2017 | _ |
| Airtel Payments Bank | New Delhi | 2017 | _ |
| Indian Post Payments Bank | New Delhi | 2018 | 650 |
List of State Co-operative banks in India
| S.No. | State Co-operative bank name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Kerala State Co-operative bank limited |
| 2 | The Maharashtra State Co-operative bank limited |
| 3 | Mizoram co-operative apex bank |
| 4 | Tamil Nadu state apex co-operative bank |
| 5 | West Bengal State Co-operative bank limited |
| 6 | The Delhi State Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 7 | Manipur State Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 8 | The Gujrat State Co-operative bank ltd. |
| 9 | Rajasthan State Co-operative Bank ltd. |
List of Urban Co-operative Banks in India
| S.No. | Urban Co-operative Bank name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Saraswat bank |
| 2 | Surat peoples coop bank limited |
| 3 | Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative Bank |
| 4 | Kalyan Janata Sahakari bank ltd. |
| 5 | New India Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 6 | NKGSB Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 7 | Nasik Merchant’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 8 | Pravara Sahakari bank limited |
| 9 | Rupee Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 10 | TJSB Sahakari bank limited |
| 11 | Nagar Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 12 | Janalaxmi Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 13 | Jalgaon Janata Sahakari Bank limited |
| 14 | Indian Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 15 | GS Mahanagar Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 16 | Greater Bombay Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 17 | Gopinath Patil Parsik Janata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 18 | Goa Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 19 | Fingrowth Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 20 | Dombivli Nagari Sahakari Bank LTD. |
| 21 | Cosmos Bank |
| 22 | Citizen Credit Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 23 | Bombay Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 24 | Bharat Co-operative Bank Mumbai Ltd. |
| 25 | Bassein Catholic Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 26 | Apna Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 27 | Andhra Pradesh Mahesh Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 28 | Amanath Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 29 | Ahmedabad Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 30 | Abhyudaya Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
