87
Algorithm of Longest Common Sequence
LCS-LENGTH (X, Y) 1. m ← length [X] 2. n ← length [Y] 3. for i ← 1 to m 4. do c [i,0] ← 0 5. for j ← 0 to m 6. do c [0,j] ← 0 7. for i ← 1 to m 8. do for j ← 1 to n 9. do if xi= yj 10. then c [i,j] ← c [i-1,j-1] + 1 11. b [i,j] ← "↖" 12. else if c[i-1,j] ≥ c[i,j-1] 13. then c [i,j] ← c [i-1,j] 14. b [i,j] ← "↑" 15. else c [i,j] ← c [i,j-1] 16. b [i,j] ← "← " 17. return c and b.
Example of Longest Common Sequence
Example: Given two sequences X [1…m] and Y [1…..n]. Find the longest common subsequences to both.

here X = (A,B,C,B,D,A,B) and Y = (B,D,C,A,B,A) m = length [X] and n = length [Y] m = 7 and n = 6 Here x1= x [1] = A y1= y [1] = B x2= B y2= D x3= C y3= C x4= B y4= A x5= D y5= B x6= A y6= A x7= B Now fill the values of c [i, j] in m x n table Initially, for i=1 to 7 c [i, 0] = 0 For j = 0 to 6 c [0, j] = 0
That is:
Now for i=1 and j = 1 x1 and y1 we get x1 ≠ y1 i.e. A ≠ B And c [i-1,j] = c [0, 1] = 0 c [i, j-1] = c [1,0 ] = 0 That is, c [i-1,j]= c [i, j-1] so c [1, 1] = 0 and b [1, 1] = ' ↑ ' Now for i=1 and j = 2 x1 and y2 we get x1 ≠ y2 i.e. A ≠ D c [i-1,j] = c [0, 2] = 0 c [i, j-1] = c [1,1 ] = 0 That is, c [i-1,j]= c [i, j-1] and c [1, 2] = 0 b [1, 2] = ' ↑ ' Now for i=1 and j = 3 x1 and y3 we get x1 ≠ y3 i.e. A ≠ C c [i-1,j] = c [0, 3] = 0 c [i, j-1] = c [1,2 ] = 0 so c [1,3] = 0 b [1,3] = ' ↑ ' Now for i=1 and j = 4 x1 and y4 we get. x1=y4 i.e A = A c [1,4] = c [1-1,4-1] + 1 = c [0, 3] + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1 c [1,4] = 1 b [1,4] = ' ↖ ' Now for i=1 and j = 5 x1 and y5 we get x1 ≠ y5 c [i-1,j] = c [0, 5] = 0 c [i, j-1] = c [1,4 ] = 1 Thus c [i, j-1] > c [i-1,j] i.e. c [1, 5] = c [i, j-1] = 1. So b [1, 5] = '←' Now for i=1 and j = 6 x1 and y6 we get x1=y6 c [1, 6] = c [1-1,6-1] + 1 = c [0, 5] + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1 c [1,6] = 1 b [1,6] = ' ↖ '
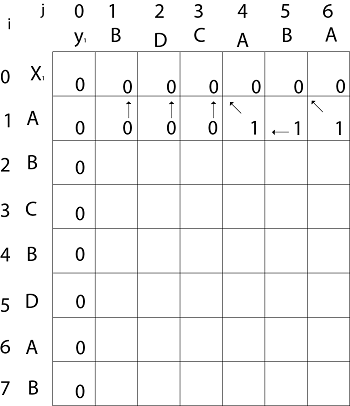
Now for i=2 and j = 1 We get x2 and y1 B = B i.e. x2= y1 c [2,1] = c [2-1,1-1] + 1 = c [1, 0] + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1 c [2, 1] = 1 and b [2, 1] = ' ↖ ' Similarly, we fill the all values of c [i, j] and we get
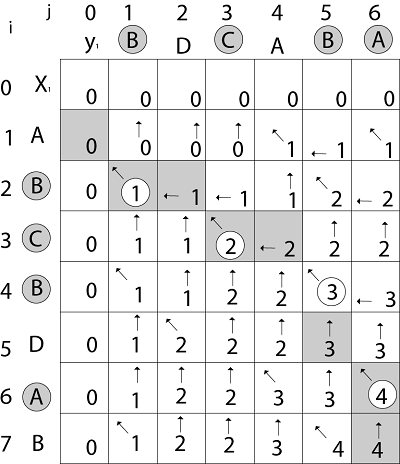
Step 4: Constructing an LCS: The initial call is PRINT-LCS (b, X, X.length, Y.length)
PRINT-LCS (b, x, i, j) 1. if i=0 or j=0 2. then return 3. if b [i,j] = ' ↖ ' 4. then PRINT-LCS (b,x,i-1,j-1) 5. print x_i 6. else if b [i,j] = ' ↑ ' 7. then PRINT-LCS (b,X,i-1,j) 8. else PRINT-LCS (b,X,i,j-1)
Example: Determine the LCS of (1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1) and (0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0).
Solution: let X = (1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1) and Y = (0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0).
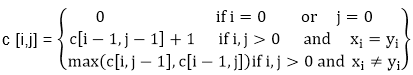
We are looking for c [8, 9]. The following table is built.
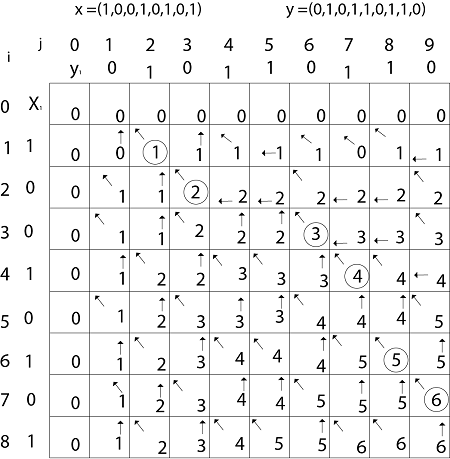
From the table we can deduct that LCS = 6. There are several such sequences, for instance (1,0,0,1,1,0) (0,1,0,1,0,1) and (0,0,1,1,0,1)
Next Topic0/1 Knapsack Problem
