Plant cell
A cell is the basic building block of a structure. It is the base of the structure of life in all organisms. Cells are present in all living organisms like humans, plants, and animals. Plants are also composed of numerous cells that have a definite structure.
Earlier, a cell was discovered on a plant cell as a living thing. Afterward, scientists found out the detailed structure of the plant under the highly defined microscope.
Let’s learn about plant cells and it’s a structure in detail.
Definition:-
A cell is of two types – Eukaryotic and prokaryotic(plant and animal both). A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell type different in several fundamental factors from the eukaryotic organisms.
Plant cells and animal cells contain similar organelles and the nucleus, but the major difference is a cell wall outside the cell membrane in a plant cell.
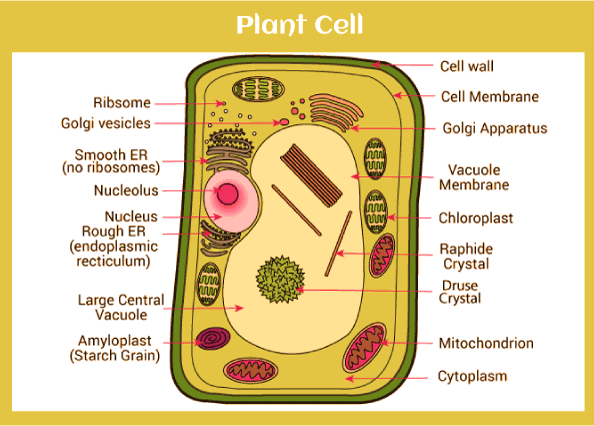
Detailed diagram of plant cell
Although both plant and animal cells share some of the same organelles, plant cells still perform different functions compared to animal cells. A plant cell is larger, and many other differences are featured in the detailed study under the microscope.
Let’s study the detailed structure of the plant cell with all the functions of the organelles. The following organelles are:-
The Cell wall
This is the outermost layer of the cell structure composed of lignin, pectin, cellulose, glycoproteins, and hemicellulose. It also consists of proteins, cellulose, and polysaccharides.
The main function of the cell wall is to provide formation and structural support to the cell. It filters the molecules passing in and out of the cells and guards mechanical stress.
Microtubules guide the formation of the cell that consist of three-layer ? primary, secondary and middle lamella. The primary cell is formed by cellulose.
Cell Membrane
This semi-permeable membrane is present within the cell wall and is composed of a thin layer of fat and protein. The cell membrane controls the entry and exit of specific substances to keep toxins from entering inside. Cell membrane transfers the essential minerals and nutrients in the cell.
Nucleus
It is only present in a eukaryotic cell. As the nucleus is a membrane-bound structure, its main function is to store DNA or hereditary information necessary for growth, cell division, and metabolism. Nucleolus manufactures cells’ protein-producing structures and ribosomes. Nucleopore allows nucleic acids and proteins to pass through the cell.
Plastids
These are the organelles that consist of their DNA. The function of plastids is to store starch, carry out the photosynthesis process. Major building blocks of cells are synthesis under the plastids.
Various kinds of plastids and their functions are below:-
Leucoplasts – These are used to store lipid, protein, and starch, and they are found in the non-photosynthesis tissues of the plant.
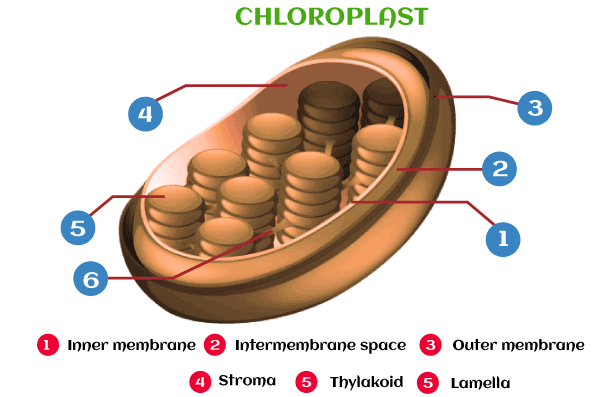
Chloroplast is an organelle (disc-shaped) enclosed by a phospholipid membrane. Fluid is present within the chloroplast named “storma,” which comprises circular DNA. The most important substance, chlorophyll (required for photosynthesis and responsible for the color of leaves), resides in the chloroplast. Chlorophyll helps transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose with the help of sunlight absorbed by it.
Chromoplasts – These kinds of plastids are responsible for storage in photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. Chromoplasts are responsible for all ripe fruits and flowers’ color as it has yellow, orange, and red color pigmentation (pigment synthesis).
Central Vacuole
Central vacuole is the largest organelle that stores materials and waste, and a membrane surrounds it. In a mature plant cell, around 30% of its volume is absorbed. It is surrounded by a membrane named tonoplast, and vacuole consists of the cell sap, a mixture of enzymes, salt, and other substances. The main function of the central vacuole is maintaining proper pressure in the plant cell by providing the proper structure for growing the plant.
Golgi Apparatus
The main function of the Golgi apparatus is to spread synthesized macromolecules to a different part of the cell and commonly known as the Golgi complex.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are generally known as protein factories of the cell as these are the smallest membrane-bound organelles that comprise protein and RNA.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria- “The powerhouse of the cell” responsible for producing energy by breaking down carbohydrate and sugar molecules. It is a double-membrane organelle present in the cytoplasm.
Lysosomes
The functional suicidal bags of the cell that manage the cellular waste disposed of by foreign bodies in the cell by digesting worn-out organelles and food particles in the cell. All the digestive enzymes are held in an enclosed membrane by lysosomes.
Characteristics of plant cell
- Plant cells consist of – a cell wall, a large central vacuole, a cell membrane, and plastids that include chloroplast, Chromoplasts, and Leucoplasts.
- Plant cell doesn’t have centrosome and lysosomes.
- Presence of nucleus
- Chromosomes have DNA, RNA, and protein,
- There is an intracellular cytoplasmic movement found in the cell.
- Various cell organelles like – endoplasmic, mitochondria, reticulum, Golgi bodies are present in all plant cells.
- A two-layered nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus.
- Mitosis division occurs in the cell, and the mitotic spindle is formed.
- Cellulose or chitin made the cell wall.
Function of cell
The major function of plant cells is the photosynthesis process. This process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cell, where food for the plant is prepared by the utilization of carbon-di-oxide, sunlight, and water.
Plant cells also help transport water and nutrients to the different parts (roots, stem, leaves). The photosynthesis process produces food in energy, a standardized form of ATP.
