Types of Adverb
What Is An Adverb?
An adverb is a term used to transform, change, or characterize other terms, such as the adjectives, the verbs, clauses, another adverb, or any other sort of string of words, except determiners and adjectives that explicitly change nouns.
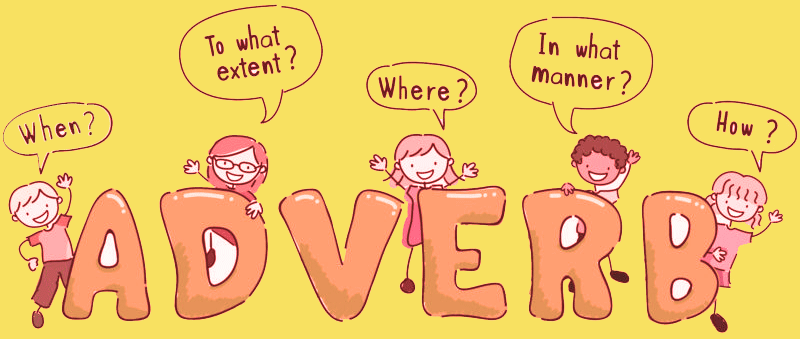
Adverbs can be thought of as words that provide context, which is a useful approach to grasp them. Adverbs, in particular, describe how, where, when, in what manner, and to what degree anything is accomplished or occurring.
Usually, we can identify an adverb by the reality that it frequently ends in -ly, but many adverbs do not. Furthermore, adverbs can be utilized in several ways.
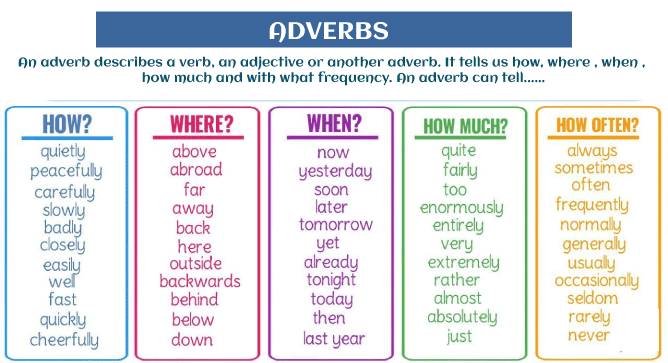
Adverbs typically serve to present a more complete picture by detailing how something occurs, such as
- When? He always comes late
- How? He drives quickly
- Where? They travel all the places together.
- In what way? He eats patiently
- To what extent? It’s extremely cold.
Types of Adverb
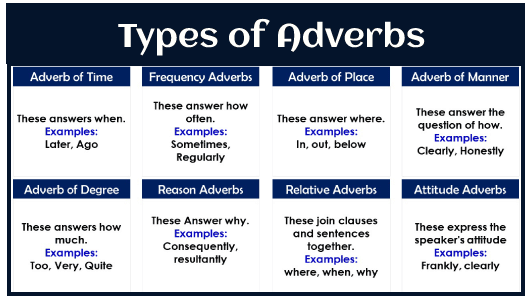
Adverbs, like all other parts of speech, like nouns and verbs, come in various forms. Adverbs are typically classified based on the types of queries they reply to or the information that they supply. Right now, we’ll have a look at the six common types of adverbs:
- Adverbs of frequency
- Adverbs of time
- Adverbs of manner
- Adverbs of degree
- Adverbs of place
- Conjunctive adverbs

Adverb Of Manner
An adverb of manner is one of the types of adverb that describes how an action is performed. Adverbs of manner are frequently adjectives with -ly attached to the ending, but that’s not always the situation. In certain way, adverbs have the same spelling as the adjectives.
Adverbs of manner encompass the following:
Slowly
Rapidly
Messily
Poorly
Quickly
Sweetly
Sadly
The instances of adverbs of manner in the following statements are highlighted for easy identification.
- Helen passed the test easily. How did she pass the test?
- They walk quickly to board the bus. How did they walk?
- The lunch celebration went badly. How was the lunch celebration?
- Jack addressed the question properly. How did Jack address the question?
Observe how the adverbs are made by adding -ly to the adjectives bad, proper, and quick, despite the fact that there is a tiny spelling shift when generating an adverb.
Adverbs are made by adding -ly to the adjectives bad, correct, and rapid, albeit there is a subtle spelling variation when an adverb is generated with the adjective easy.
As previously stated, most of the adverbs of manner use the same spelling as the adjectives and never terminate in a -ly:
- The kids had worked
- The car drives hard.
- Julie twirls well.
Adverbs Of Place
An adverb of place, also known as a spatial adverb, is one of the types of adverb that will help to clarify where an action takes place. Position adverbs will be related to the verb’s action in a statement, giving context for directions, distance, and position: south, everywhere, up, right, nearby, back, within, around. These words do not typically finish in -ly.
Adverbs of location are described in the subsequent texts for ease of identification.
Directions
- New York is situated to the north of Philadelphia.
- They made their way down the hillside.
- I tried here first, then there, but I cannot find them anywhere.
Observe that here, and there are types of adverb that are mostly used at the start of a statement to articulate intense focus or in exclamation.
- Here comes the moon.
- There is romance in the wind.
- Here you are!
Adverbs of place are frequently employed as prepositions. The distinction is that when employed as an adverb, the phrase modifies a verb; when employed as a preposition, it’s often accompanied by a noun.
- Kashmir is located in the north of Punjab -> Kashmir is marked on the map.
- They traveled down the stream -> They traveled in the first class.
- That dog was strolling around by itself-> We put a bell around its torso.
Distance
Next comes the distance; let us have a look at a few examples;
- There was a dog close by
- Janie is heading far away.
- Carl is sitting closeto us.
Position
Next in this category is the position; let us look at the examples;
- The map lies underneaththe carpet.
- The kitty is resting on the couch.
- Why are you sitting in the middle of the ground?
Furthermore, some position adverbs are one of the types of adverb that will relate to a direction of motion. These are frequently suffixed with -ward or -wards.
- Oscinary toured onwardto Southern California.
- Annie glanced upwardsto the sky.
Mary, move forward to the front of the security line, please.
Frequency Adverbs(When occurred?)
Adverb of frequency is one of the types of adverb that are employed to signify time or the frequency with which something happens. Adverbs of frequency can be demarcated into two classes. The first, adverbs of uncertain frequency, are phrases with ambiguous meanings regarding how long or how frequently something occurs: usually, always, normally. Adverbs like these are normally put after the primary verb or between the auxiliary verb and the infinitive.
Adverbs of frequency are highlighted in the below-mentioned statements for easy identification.
- The adverb is usuallylocated prior to the primary verb.
- I can typically make the painting.
- I will alwayscherish
Adverbs with a fixed frequency are normally put at the conclusion of a statement.
- They get paid hourly.
- I come here monthly.
Adverb of Time(When performed?)
Next in the list of types of adverb is that of time. Time adverbs are typically used towards the end of the statement. While adverbs of timeshare some similarities to adverbs of frequency, they notify us whenever something happens.
Adverbs of time are highlighted in the following statements for easy recognition.
- I will see you tomorrow.
- Peter missed his lunch both yesterday and today.
- They have to go now.
- We initially met Lucy last year.
While it is nearly often correct to position the adverb of time at the end of the statement, if it is crucial to the situation, you can position this as one of the types of adverb at the beginning of the statement to put a different focus on time.
These have been highlighted for easy recognition in the following statements.
- Last year was the memorable year of our lives.
- Tomorrow our destiny will be secured.
- Yesterday my challenges seemed impossible to overcome.
- The scenario seems to change weekly
- The publication is bought daily.
Purpose Adverbs (Some English experts consider this also as a type of adverb)
Adverbs of purpose, often known as adverbs of reason, is one of the types of adverb that help to explain why something happened. They can be independent terms – so, because, thus, since – or phrases – so that, in order to.
Notice how the adverbs of purpose are employed to connect phrases that would not make sense if created alone in the instances.
Examples of purpose adverbs are highlighted in the below-mentioned statements for easy identification.
- I was tired this morning; thus, I didn’t go to school.
- I began running so that I wouldn’t be late.
- SinceI was late, I ran a little quicker.
- I’ll get you a present becauseit’s your birthday.
Degree Adverbs (How Much?)
Adverbs of degree are is one of the types of adverb that reflect the importance/degree/level of the action in the statement. They provide an answer to the inquiry, “How much is the action done?”
Completely, almost, entirely, less, moderately, most, thoroughly, somewhat, extremely, much, and so on are examples of degree adverbs. These have been highlighted for easy recognition in the following statements.
Example:
- Elizabeth completelyforgot about her annual celebration.
- I read the paper thoroughly.
- I am so happy about the upcoming job.
- Robert hardlyexperiments
Adverbs of degree, in general, convey the magnitude of an action or quality. These adverbs are frequently used to characterize adjective and other adverb as intensifier.
Conjunctive Adverbs:
A conjunctive adverb is one of the types of adverb that joins two or more phrases or sentences. It illustrates relationships and enables transitions between ideas.
Connectors are another name for conjunctive adverbs. These have been highlighted for easy recognition in the following statements.

Example:
- Last night it poured. Nonetheless, the championship game has not been canceled.
- We are still unsure, however, if the officials will come.
- Last summer, there was a great drought; consequently, we could not get enough food.
Add adverbs when required.
Now that you understand the types of adverb feel free to use them wisely in your writing. Suppose you identify a situation where you can use one powerful verb instead of an adverb and a medium power verb, then in that situation utilise the singular verb. Otherwise, your text may become overly dense and difficult to read.
Moreover, at times you may find it difficult to use it, but the key to using the right set of adverbs at the right time is practice. So practice frequently. So that you get the grasp of it; thus, keep learning and practicing.
