Types of Transmission
The transmission mode is a computer network process in which data or information is transmitted between two devices over the network. We can also say that it is a mechanism that transfers data in electromagnetic bits format between two devices that are connected through network. It is also known as communication mode.
The transmission mode defines the direction of the flow of the data. For example, a sender wants to send data to a particular receiver, then the sender can send information to a receiver using transmission mode over the network.
In this section, we will focus on types of transmission.
Transmission Modes
There are following three types of transmission modes .in network.
- Simplex Mode
- Half duplex Mode
- Full duplex Mode
Simplex Mode
It is a basic mode of transmission that enables the transmission of data only in one direction. When the data is transferring to the other side, the other person can only receive the data but cannot respond to the message at the same time. Simplex mode is also called a unidirectional mode. The examples of simplex mode are keyboard, monitor, television, and radio etc.
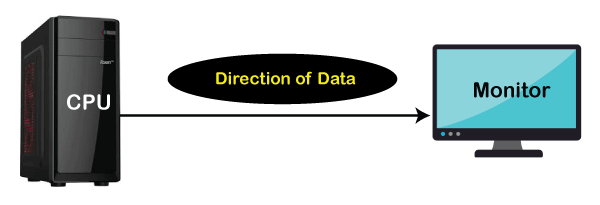
Advantage of Simplex Mode:
- It uses the full capacity of bandwidth during transmission of data due to single directional.
- There are no traffic issues occur during communication.
Disadvantage of Simplex Mode:
- Transmission of data in only one direction weaker the performance of simplex mode.
- Two devices cannot communicate with each other in at the same time.
- Bidirectional transmission is not occurring in the simplex mode.
Half Duplex Mode
Half-duplex mode transfers data in both directions but not at the same time. We can also say it is a way of communication in which sender sends the information to the receiver, and the receiver can receive the information. After receiving the information, the receiver can respond to the sender. The walkie talkie is the best example of half duplex mode. In this device, when the sender completes his message speaks over and out which indicates that the receiver can responds to the message now.
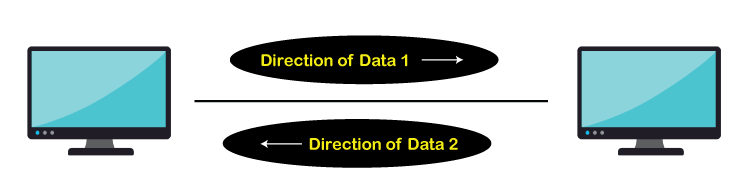
Advantage of Half Duplex Mode:
- It is a two-dimensional model of transmission of the data.
- In half-duplex mode, data can be received or sent from both directions but only one at a time.
- The transmission of data is easy as compared to the simplex mode.
- It requires less complicated hardware.
- There is less congestion in the network.
Disadvantage of Half Duplex Mode:
- When one device sends data to another device, the second one must wait for that may cause delays in receiving the output.
- Slow in the transmission of data.
- The speed of half-duplex mode is slower than the full-duplex mode of transmission.
- Data cannot simultaneously send or receive by the sender and the receiver.
Full Duplex Mode
Full-duplex mode allows the transmission of data between the two devices at the same time. It is also known as a bidirectional mode. The sender and receiver can simultaneously send and receive the data over a network. For example, in a telephonic conversation, two people can talk and listen simultaneously at the same time.

Advantage of Full Duplex Mode:
- The performance of a full-duplex transmission mode is much higher than the simplex and the half-duplex mode.
- The bandwidth of full-duplex mode is double during the transmission of the data.
- Both devices can send or receive the data simultaneously.
- There is no delay in transmitting data over the network.
Disadvantage of Full Duplex Mode:
- In full-duplex mode, there can be a traffic problem while transmitting the data on a network.
- There is no proper utilization of bandwidth in full-duplex mode while sending or receiving data at the same time.
Simplex Vs. Half Duplex Vs. Full Duplex Mode
| Simplex Mode | Half Duplex Mode | Full Duplex Mode |
|---|---|---|
| It is a unidirectional mode of transmission in which the flow of data only in one direction. | It is a bidirectional mode of transmission in which data flows in two ways but one at a time. | It is also a two-way or bidirectional mode of transmission in which data flows in two ways at the same time. |
| One sender can only send data, but the other end-user cannot respond. | Both can send and respond to information but not at the same time. | Both can simultaneously send or receive messages on the same network at the same time. |
| The performance of the simplex mode is slow as compared to Half and Full-Duplex mode of transmission. | Half-duplex mode performance is higher than simplex mode but slower than full-duplex. | The performance of full-duplex mode is much higher than both simplex and half-duplex mode. |
| The bandwidth usage is maximum. | The bandwidth usage during data transmission is low. | The bandwidth usage during data transmission is double. |
| Example: monitor, radio, keyboard, mouse and the television. | Example: walkie-talkie. | Example: telecommunication, mobile, etc. |
