Stacking in Machine Learning
There are many ways to ensemble models in machine learning, such as Bagging, Boosting, and stacking. Stacking is one of the most popular ensemble machine learning techniques used to predict multiple nodes to build a new model and improve model performance. Stacking enables us to train multiple models to solve similar problems, and based on their combined output, it builds a new model with improved performance.
In this topic, “Stacking in Machine Learning“, we will discuss a few important concepts related to stacking, the general architecture of stacking, important key points to implement stacking, and how stacking differs from bagging and boosting in machine learning. Before starting this topic, first, understand the concepts of the ensemble in machine learning. So, let’s start with the definition of ensemble learning in machine learning.
What is Ensemble learning in Machine Learning?
Ensemble learning is one of the most powerful machine learning techniques that use the combined output of two or more models/weak learners and solve a particular computational intelligence problem. E.g., a Random Forest algorithm is an ensemble of various decision trees combined.
Ensemble learning is primarily used to improve the model performance, such as classification, prediction, function approximation, etc. In simple words, we can summarise the ensemble learning as follows:
“An ensembled model is a machine learning model that combines the predictions from two or more models.”
There are 3 most common ensemble learning methods in machine learning. These are as follows:
- Bagging
- Boosting
- Stacking
However, we will mainly discuss Stacking on this topic.
1. Bagging
Bagging is a method of ensemble modeling, which is primarily used to solve supervised machine learning problems. It is generally completed in two steps as follows:
- Bootstrapping: It is a random sampling method that is used to derive samples from the data using the replacement procedure. In this method, first, random data samples are fed to the primary model, and then a base learning algorithm is run on the samples to complete the learning process.
- Aggregation: This is a step that involves the process of combining the output of all base models and, based on their output, predicting an aggregate result with greater accuracy and reduced variance.
Example: In the Random Forest method, predictions from multiple decision trees are ensembled parallelly. Further, in regression problems, we use an average of these predictions to get the final output, whereas, in classification problems, the model is selected as the predicted class.
2. Boosting
Boosting is an ensemble method that enables each member to learn from the preceding member’s mistakes and make better predictions for the future. Unlike the bagging method, in boosting, all base learners (weak) are arranged in a sequential format so that they can learn from the mistakes of their preceding learner. Hence, in this way, all weak learners get turned into strong learners and make a better predictive model with significantly improved performance.
We have a basic understanding of ensemble techniques in machine learning and their two common methods, i.e., bagging and boosting. Now, let’s discuss a different paradigm of ensemble learning, i.e., Stacking.
3. Stacking
Stacking is one of the popular ensemble modeling techniques in machine learning. Various weak learners are ensembled in a parallel manner in such a way that by combining them with Meta learners, we can predict better predictions for the future.
This ensemble technique works by applying input of combined multiple weak learners’ predictions and Meta learners so that a better output prediction model can be achieved.
In stacking, an algorithm takes the outputs of sub-models as input and attempts to learn how to best combine the input predictions to make a better output prediction.
Stacking is also known as a stacked generalization and is an extended form of the Model Averaging Ensemble technique in which all sub-models equally participate as per their performance weights and build a new model with better predictions. This new model is stacked up on top of the others; this is the reason why it is named stacking.
Architecture of Stacking
The architecture of the stacking model is designed in such as way that it consists of two or more base/learner’s models and a meta-model that combines the predictions of the base models. These base models are called level 0 models, and the meta-model is known as the level 1 model. So, the Stacking ensemble method includes original (training) data, primary level models, primary level prediction, secondary level model, and final prediction. The basic architecture of stacking can be represented as shown below the image.
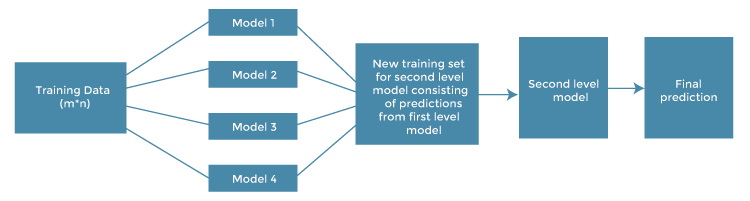
- Original data: This data is divided into n-folds and is also considered test data or training data.
- Base models: These models are also referred to as level-0 models. These models use training data and provide compiled predictions (level-0) as an output.
- Level-0 Predictions: Each base model is triggered on some training data and provides different predictions, which are known as level-0 predictions.
- Meta Model: The architecture of the stacking model consists of one meta-model, which helps to best combine the predictions of the base models. The meta-model is also known as the level-1 model.
- Level-1 Prediction: The meta-model learns how to best combine the predictions of the base models and is trained on different predictions made by individual base models, i.e., data not used to train the base models are fed to the meta-model, predictions are made, and these predictions, along with the expected outputs, provide the input and output pairs of the training dataset used to fit the meta-model.
Steps to implement Stacking models:
There are some important steps to implementing stacking models in machine learning. These are as follows:
- Split training data sets into n-folds using the RepeatedStratifiedKFold as this is the most common approach to preparing training datasets for meta-models.
- Now the base model is fitted with the first fold, which is n-1, and it will make predictions for the nth folds.
- The prediction made in the above step is added to the x1_train list.
- Repeat steps 2 & 3 for remaining n-1folds, so it will give x1_train array of size n,
- Now, the model is trained on all the n parts, which will make predictions for the sample data.
- Add this prediction to the y1_test list.
- In the same way, we can find x2_train, y2_test, x3_train, and y3_test by using Model 2 and 3 for training, respectively, to get Level 2 predictions.
- Now train the Meta model on level 1 prediction, where these predictions will be used as features for the model.
- Finally, Meta learners can now be used to make a prediction on test data in the stacking model.
Stacking Ensemble Family
There are some other ensemble techniques that can be considered the forerunner of the stacking method. For better understanding, we have divided them into the different frameworks of essential stacking so that we can easily understand the differences between methods and the uniqueness of each technique. Let’s discuss a few commonly used ensemble techniques related to stacking.
Voting ensembles:
This is one of the simplest stacking ensemble methods, which uses different algorithms to prepare all members individually. Unlike the stacking method, the voting ensemble uses simple statistics instead of learning how to best combine predictions from base models separately.
It is significant to solve regression problems where we need to predict the mean or median of the predictions from base models. Further, it is also helpful in various classification problems according to the total votes received for prediction. The label with the higher numbers of votes is referred to as hard voting, whereas the label that receives the largest sums of probability or lesser votes is referred to as soft voting.
The voting ensemble differs from than stacking ensemble in terms of weighing models based on each member’s performance because here, all models are considered to have the same skill levels.
Member Assessment: In the voting ensemble, all members are assumed to have the same skill sets.
Combine with Model: Instead of using combined prediction from each member, it uses simple statistics to get the final prediction, e.g., mean or median.
Weighted Average Ensemble
The weighted average ensemble is considered the next level of the voting ensemble, which uses a diverse collection of model types as contributing members. This method uses some training datasets to find the average weight of each ensemble member based on their performance. An improvement over this naive approach is to weigh each member based on its performance on a hold-out dataset, such as a validation set or out-of-fold predictions during k-fold cross-validation. Furthermore, it may also involve tuning the coefficient weightings for each model using an optimization algorithm and performance on a holdout dataset.
Member Assessment: Weighted average ensemble method uses member performance based on the training dataset.
Combine With Model: It considers the weighted average of prediction from each member separately.
Blending Ensemble:
Blending is a similar approach to stacking with a specific configuration. It is considered a stacking method that uses k-fold cross-validation to prepare out-of-sample predictions for the meta-model. In this method, the training dataset is first to split into different training sets and validation sets then we train learner models on the training sets. Further, predictions are made on the validation set and sample set, where validation predictions are used as features to build a new model, which is later used to make final predictions on the test set using the prediction values as features.
Member Predictions: The blending stacking ensemble uses out-of-sample predictions on a validation set.
Combine With Model: Linear model (e.g., linear regression or logistic regression).
Super Learner Ensemble:
This method is quite similar to blending, which has a specific configuration of a stacking ensemble. It uses out-of-fold predictions from learner models and prepares a meta-model. However, it is considered a modified form of blending, which only differs in the selection of how out-of-sample predictions are prepared for the meta learner.
Summary of Stacking Ensemble
Stacking is an ensemble method that enables the model to learn how to use combine predictions given by learner models with meta-models and prepare a final model with accurate prediction. The main benefit of stacking ensemble is that it can shield the capabilities of a range of well-performing models to solve classification and regression problems. Further, it helps to prepare a better model having better predictions than all individual models. In this topic, we have learned various ensemble techniques and their definitions, the stacking ensemble method, the architecture of stacking models, and steps to implement stacking models in machine learning.
