Linux Cat Command
The ‘cat’ command is the most universal and powerful tool. It is considered to be one of the most frequently used commands. It can be used to display the content of a file, copy content from one file to another, concatenate the contents of multiple files, display the line number, display $ at the end of the line, etc.
Linux cat command: to display file content
The ‘cat’ command can be used to display the content of a file.
Syntax:
Example:
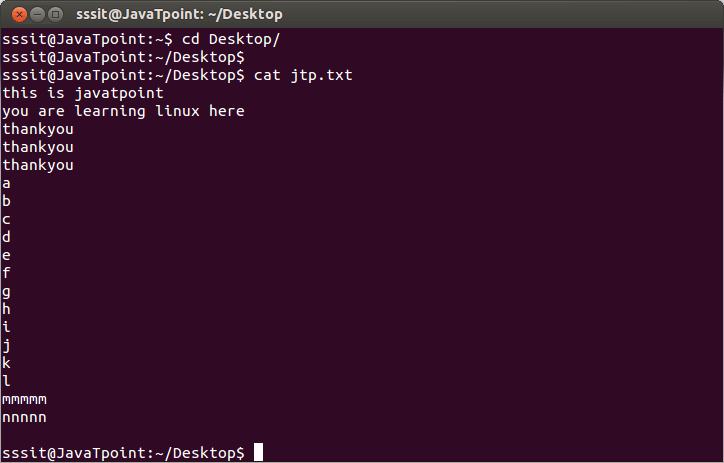
In the above snapshot, file ‘jtp.txt’ is displayed with the help of command “cat jtp.txt”.
Note: To display the content of multiple files at once, type file names in one single line like “cat file1 file2 file3… fileN.
Linux cat command usage
| Option | Function |
|---|---|
| cat > [fileName] | To create a file. |
| cat [oldfile] > [newfile] | To copy content from older to new file. |
| cat [file1 file2 and so on] > [new file name] | To concatenate contents of multiple files into one. |
| cat -n/cat -b [fileName] | To display line numbers. |
| cat -e [fileName] | To display $ character at the end of each line. |
| cat [fileName] <<EOF | Used as page end marker. |
Linux cat command (to create a file)
The ‘cat’ command can be used to create a new file with greater than sign (>).
Syntax:
Example:
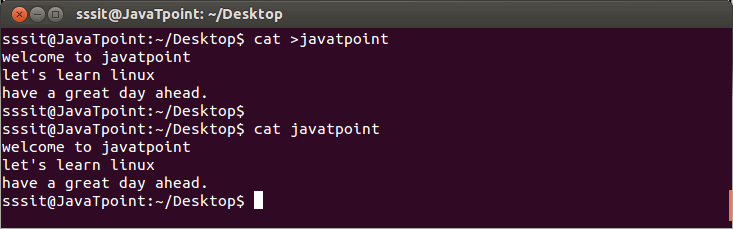
In the above snapshot, we have created a new file called “tutoraspire”. Now let’s see how to create it.
Type the command “cat >tutoraspire” and press ‘enter’. You will be directed to the next line.
Press ‘enter’ after every line and you will be directed to the next line. To save your file, go to the next line, press ‘ctrl+d’ and your file will be saved.
To Append the Content of A File
The ‘cat’ command with double greater than sign (>>) append (add something in the last of a file) something in your already existing file.
Syntax:
Example:
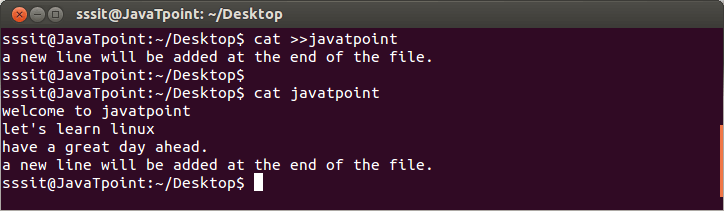
Look at the above snapshot, a new line at the end is added in the file ‘tutoraspire’. After passing “cat >> tutoraspire” command, type the lines as much as you want to add. To save the file press ‘ctrl + d’.
Linux cat command (to copy file)
The ‘cat’ command can be used to copy the content of a file into another file.
Syntax:
Example:
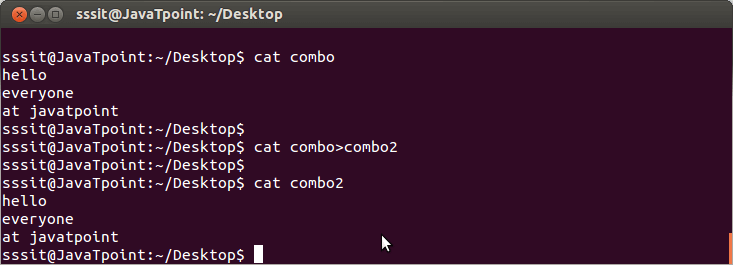
In the above snapshot, we have copied the content of file ‘combo’ into the file ‘combo2’ with the command “cat combo > combo2”.
Linux cat command (to concatenate files)
The ‘cat’ command can be used to concatenate the contents of multiple files in a single new file.
Syntax:
Example:
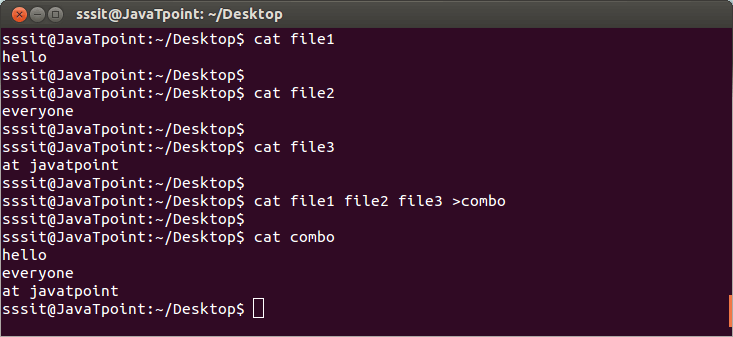
Look at the above snapshot, we have combined three files “file1, file2, and file3” into a single file “combo” with the command “cat file1 file2 file3 >combo”.
Notice the content of three separate files and then the content of a new concatenated file that is “combo”.
To Insert A New Line
A new line will be inserted while concatenating multiple files by using a hyphen (-).
syntax:
Example:
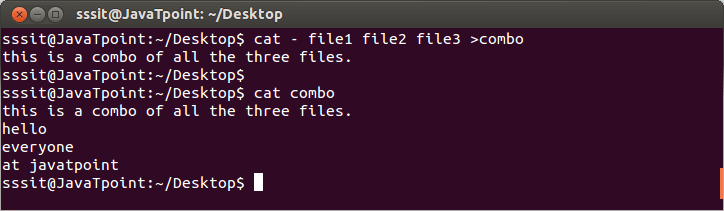
In the above snapshot, we have inserted a new line at the beginning while concatenating file1, file2 and file3 with the command “cat – file1 file2 file3 >combo”.
Note: Line will be inserted at the beginning of the file only.
Linux cat -n command (to display line numbers)
The ‘cat -n’ option displays line numbers in front of each line in a file.
Syntax:
Example:
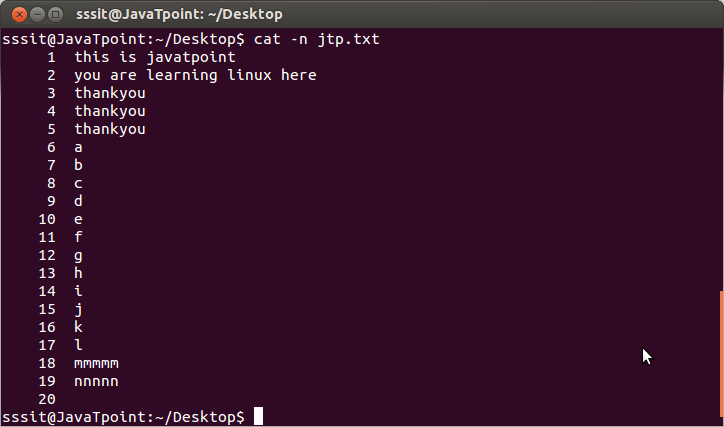
Look at the above snapshot; the file ‘jtp.txt’ has a line number in front of every line by passing the command “cat -n jtp.txt”.
cat -b (file name)
The ‘cat -b’ option removes the empty lines.
Syntax:
Example:
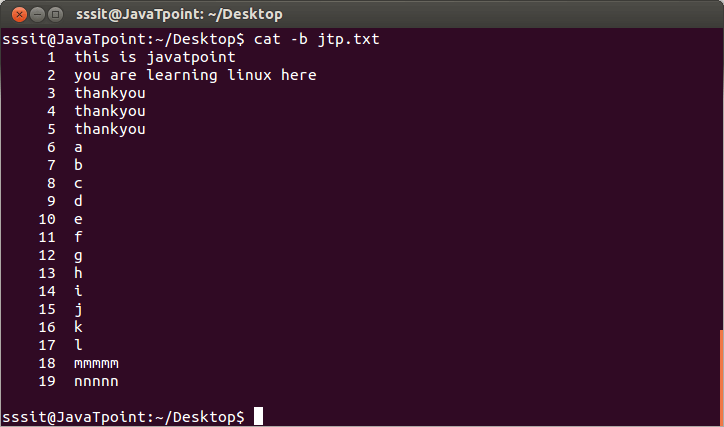
In the previous snapshot, after line 19, line number 20 has also been marked but it is an empty line.
In the above snapshot, line 20 is removed with the help of command “cat -b jtp.txt”.
Linux cat -e command (to display $)
The ‘cat-e’ option displays a ‘$’ sign at the end of every line.
Syntax:
Example:
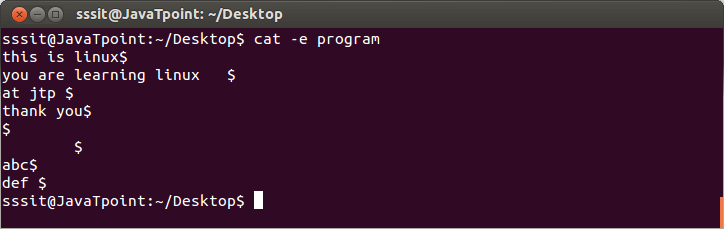
Look at the above snapshot; some lines include spaces also. A user won’t be able to recognize whitespace at the end of each line. The “cat -e program” command will put the $ sign at the end of every line including spaces.
Linux cat command (as an end marker)
The ‘cat << EOF ‘ option displays an end marker at the end of a file. It is called here directive and file content will be saved at the given end marker.
The file can be saved with the help of ‘ctrl + d ‘ keys also. It works like the end marker.
Note: Any word other than ‘EOF’ can be used for the end marker.
Syntax:
Example:
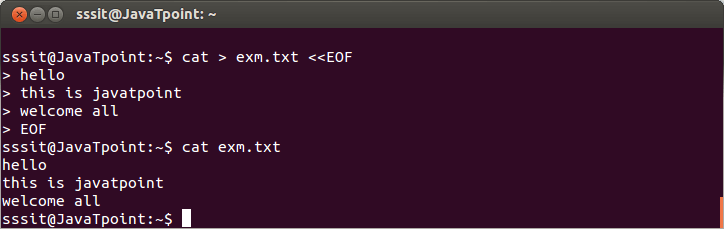
In the above snapshot, we have created ‘exm.txt’ file with ‘EOF’ as the end marker by passing the command “cat > exm.txt << EOF”.
Linux Cat Filters
When cat command is used inside pipes, it does nothing except moving stdin to stout.
Syntax:
Example:
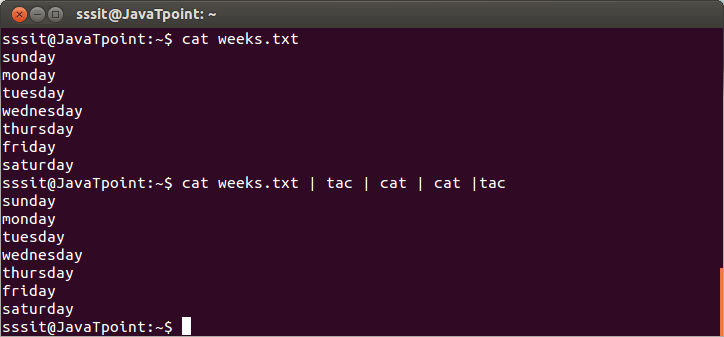
Look at the above snapshot, the output of one ‘cat’ or ‘tac’ command is passing onto another as input.
