97
Linux ps
The ps command is used to view currently running processes on the system. It helps us to determine which process is doing what in our system, how much memory it is using, how much CPU space it occupies, user ID, command name, etc .
The ps command may display different results for different systems because it displays information about the currently running process of a system.
Syntax:
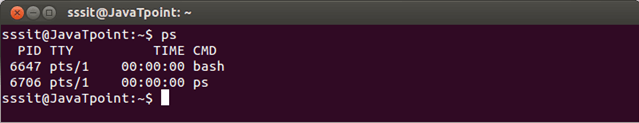
Look at the above snapshot, 4 columns are displayed as the output.
- PID is the process ID of running command
- TTY is the type of terminal where current command is running
- TIME tells how much time is used by CPU to run the process
- CMD is current command
ps command supports 3 types of usage syntax style
- Unix, may be grouped and preceded by hyphen
- BSD, may be grouped but not preceded by hyphen
- GNU, long options and preceded by double hyphens
Options
| Option | Function |
|---|---|
| ps -ef/ ps -aux | List currently running process in full format |
| ps -ax | List currently running process |
| ps -u <username> | List process for specific user |
| ps -C <command> | List process for given command |
| ps -p <PID> | List process with given PID |
| ps -ppid <PPID> | List process with given ppid |
| pstree | Show process in hierarchy |
| ps -L | List all threads for a particular process |
| ps –sort pmem | Find memory leak |
| ps -eo | Show security information |
| ps -U root -u root u | Show process running by root |
Next TopicList running process in full format
