Linux Set Environment Variable
The environment variables are dynamic values that are stored within a system and used by applications launched in shells or sub-shells. These variables have a name and their respected value. The environment variable customizes the system performance and the behavior of an application.
The environment is the track for a computer application to interact with the system. The environment variable can have information about the default applications of the system, the system locale, the path of the executable file and the keyboard layout setting, and more. The environment variable makes an app available as per the system.
Common Environment Variables
Some standard environment variables are as follows:
- PATH
This variable contains a list of directories in which our system looks for files. It separates directories by a (:) colon.
- USER
This variable holds the username.
- HOME
This variable holds the default path to the user’s home directory.
- EDITOR
This variable contains the path to the specified editor.
- UID
This variable contains the path to the user’s unique id.
- TERM
This variable contains the path to the default terminal emulator.
- SHELL
This variable contains the path to the default shell that is being used by the user.
- ENV
This variable displays all the environment variable.
How to set Environment Variable in Linux?
There are multiple commands in Linux that allow us to set and create the environment variable.
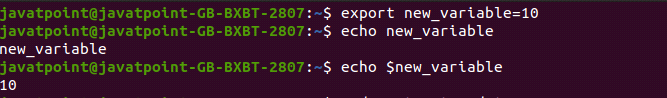
Use the export command to set a new environment variable.
To create a new variable, use the export command followed by a variable name and its value.
Syntax:
To create a new variable say new_variable, execute the command as follows:
The echo command is used to display the variable:
To display the value of the variable, use the $ symbol before the variable name:
Consider the below output:
To set Java Environment Variable, execute the command as follows:
We can also create a user to define a variable by directly declaring it on the terminal.
If we want to create a variable new_variable2, we can create it as follows:
Consider the below output:

Accessing the value of Environment Variable
To access the value of a variable, execute the echo command as follows:
Note: The variables are case sensitive; we cannot use any variable name ‘new_variable’ as ‘New_variable.’
The env command
The env command is used to display all the available variables in the system.
Output:
SHELL=/bin/bash SESSION_MANAGER=local/tutoraspire-GB-BXBT-2807:@/tmp/.ICE-unix/1458,unix/tutoraspire-GB-BXBT-2807:/tmp/.ICE-unix/1458 COLORTERM=truecolor XDG_CONFIG_DIRS=/etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu:/etc/xdg XDG_MENU_PREFIX=gnome- GNOME_DESKTOP_SESSION_ID=this-is-deprecated GTK_IM_MODULE=ibus LANGUAGE=en_IN:en QT4_IM_MODULE=ibus MANDATORY_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.mandatory.path GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=ubuntu SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/run/user/1000/keyring/ssh [email protected]=ibus DESKTOP_SESSION=ubuntu SSH_AGENT_PID=1362 GTK_MODULES=gail:atk-bridge PWD=/home/tutoraspire LOGNAME=tutoraspire XDG_SESSION_DESKTOP=ubuntu XDG_SESSION_TYPE=x11 GPG_AGENT_INFO=/run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent:0:1 XAUTHORITY=/run/user/1000/gdm/Xauthority GJS_DEBUG_TOPICS=JS ERROR;JS LOG WINDOWPATH=2 HOME=/home/tutoraspire USERNAME=tutoraspire IM_CONFIG_PHASE=1 LANG=en_IN LS_COLORS=rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:mi=00:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arc=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lha=01;31:*.lz4=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.tzo=01;31:*.t7z=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lrz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.lzo=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.zst=01;31:*.tzst=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.alz=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.cab=01;31:*.wim=01;31:*.swm=01;31:*.dwm=01;31:*.esd=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.mjpg=01;35:*.mjpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=00;36:*.au=00;36:*.flac=00;36:*.m4a=00;36:*.mid=00;36:*.midi=00;36:*.mka=00;36:*.mp3=00;36:*.mpc=00;36:*.ogg=00;36:*.ra=00;36:*.wav=00;36:*.oga=00;36:*.opus=00;36:*.spx=00;36:*.xspf=00;36: XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP=ubuntu:GNOME VTE_VERSION=5802 GNOME_TERMINAL_SCREEN=/org/gnome/Terminal/screen/dc6e48ed_7868_43d5_a086_fd6d6a90a74a INVOCATION_ID=fadf556d1cf5422ea55b247bf57c3c99 MANAGERPID=1252 CLUTTER_IM_MODULE=ibus GJS_DEBUG_OUTPUT=stderr LESSCLOSE=/usr/bin/lesspipe %s %s XDG_SESSION_CLASS=user TERM=xterm-256color DEFAULTS_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.default.path LESSOPEN=| /usr/bin/lesspipe %s USER=tutoraspire GNOME_TERMINAL_SERVICE=:1.216 DISPLAY=:0 SHLVL=1 QT_IM_MODULE=ibus XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/1000 JOURNAL_STREAM=9:35179 XDG_DATA_DIRS=/usr/share/ubuntu:/usr/local/share/:/usr/share/:/var/lib/snapd/desktop PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin GDMSESSION=ubuntu DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:path=/run/user/1000/bus _=/usr/bin/env [email protected]:~$
Removing an Environment Variable
By removing an environment variable we can remove all existing component of particular variable.
To remove an environment variable, execute the unset command followed by variable name:
The above command will delete the specified variable and its components from the system.
To remove a variable new_variable from the system, execute the command as follows:
Consider the below output:

