top
The top command displays all the running process within the environment of your system. It helps in monitoring system usage and performances. It is mainly used to detect load on the server by system administrators.
Syntax:
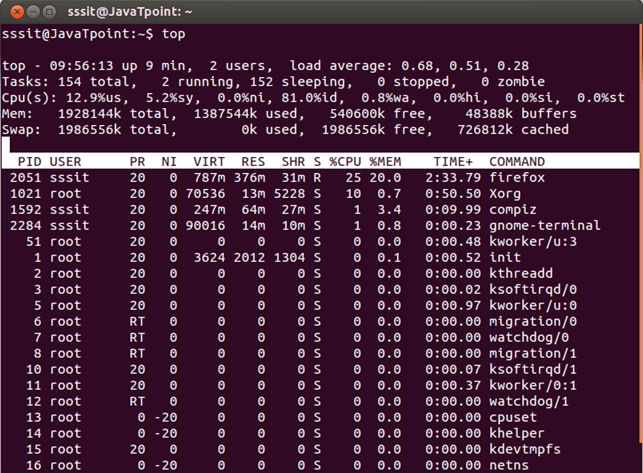
Look at the above snapshot, its output is explained here,
Line1
- Time
- how long system is running
- how many users are logged in
- and load average
Line2
- Total number of tasks
- number of running tasks
- number of sleeping tasks
- number of stopped tasks
- and number of zombie tasks
Line3
It shows CPU usage in percentage for
- users
- system
- low priority processes
- idle processes
- io wait
- hardware interrupts
- software interrupts
- steal time
Line4
It shows memory usage in kilobytes for
- total memory
- used memory
- free memory
- buffered memory
Line5
It shows swap memory usage in kilobytes for
- total memory
- used memory
- free memory
- cached memory
Table explanation
- proces ID
- user
- priority
- nice user
- virtual memory
- resident memory
- shareable memory
- CPU used percentage
- memory used percentage
- time a process has run
- command
If you want you can hide/show these header lines by pressing some keys.
For example,
press l – to show/hide Line1. Top line
press t – to show/hide Line3. CPU information
press m – to show/hide Line4 and 5. Memory information
Keeping top command running in background
You can keep top command running in the background continuously without typing top in terminal every time.
Use ctrl+z keys to get back your terminal.
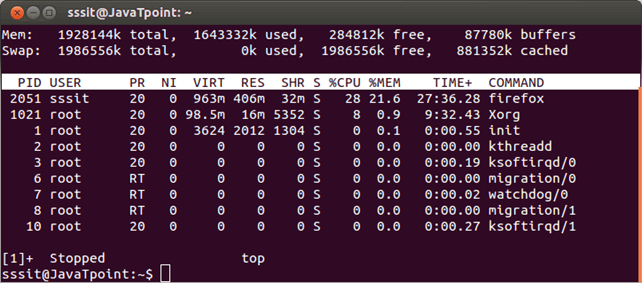
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing ctrl+z keys top command has stopped and we got our terminal back.
To bring back top command in terminal type fg in terminal.
Sorting top output
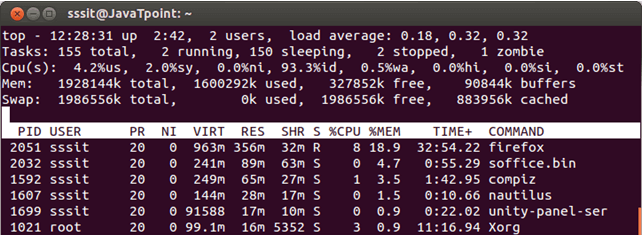
By default, top command always display output in the order of CPU usage.
Press M ? To display in order of memory usage.
Press O ? To display all possible columns that you can sort.
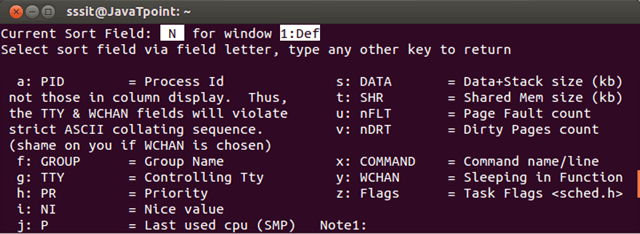
Look at the above snapshot, all the columns are assigned an alphabetic letter. To sort by column type the respective alphabet and output will be sorted according to that column.
In the first line, current sort field is shown that is N which means currently it is sorted according to column N.
Press R ? To display in reverse order.
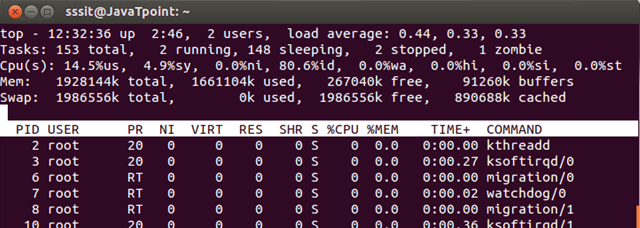
Killing a task without exiting from top
A task can be stopped without exiting from top command by pressing k key.
It will ask for task’s PID number, if you’ll have authority to kill that task, then task will be removed. Otherwise, your command will fail.
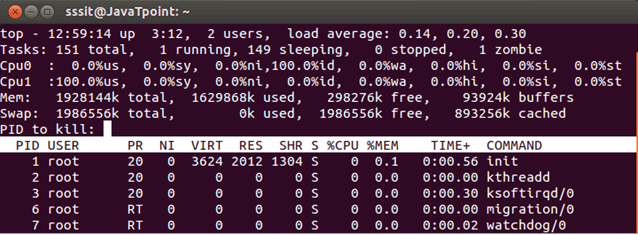
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing k, we got a message asking for PID of task to be killed.
Renice a task
Renice is done to change the scheduling order. By pressing r, you can change the priority of a process without killing it. It will also ask for PID of the process.
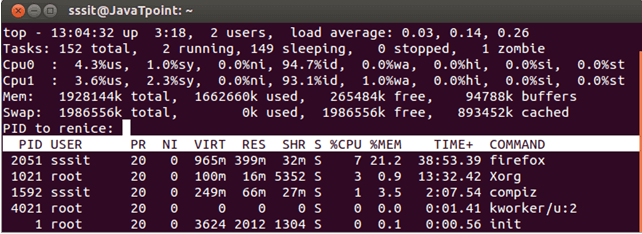
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing r, we got a message asking for PID of task to be reniced.
Display processes for selected user
In top command output you can display all the processes for a particular user only by two options. One through command line and other without existing top.
In command line, use the following command
Syntax:
Example:
top -u sssit
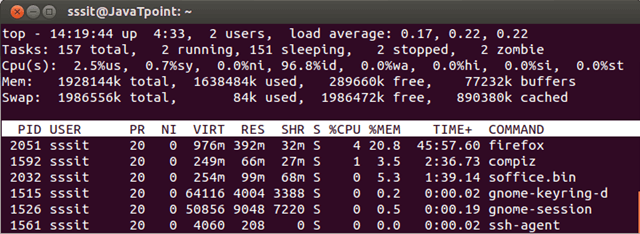
Look at the above snapshot, it displays all the processes only for user sssit.
When top command is running, press u, it will ask for username. Type the username and press enter.
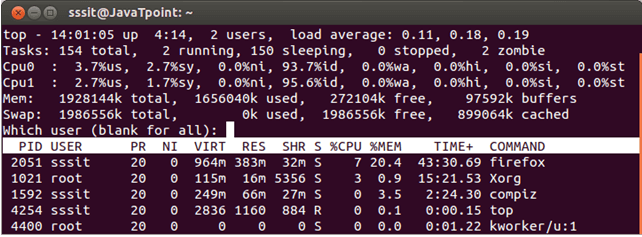
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing u, it is asking for username.
Updating top output
By default, top output is updated after every 3 seconds. When you want to update it in between 3 seconds press space bar.
You can also change updating frequency by pressing d key while running top command.
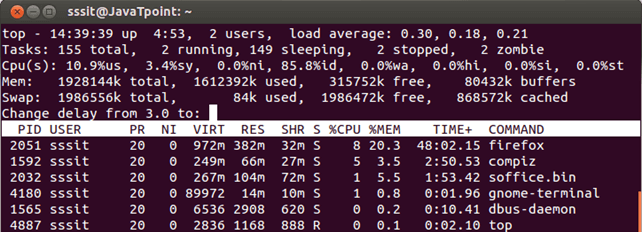
Look at the above snapshot, after pressing d key, it is asking for time for which it will be frequently updated.
Changing colors
Colors can be changed by pressing z key and text can be made bold by pressing b key.
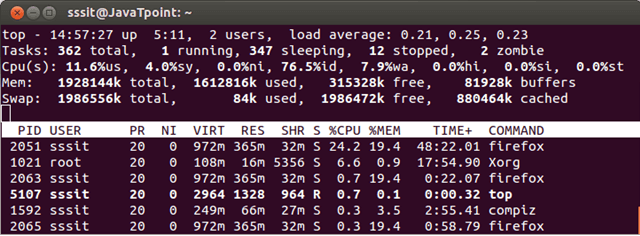
Look at the above snapshot, by pressing b all running processes are highlighted in white.
To change color press z (small z) key.
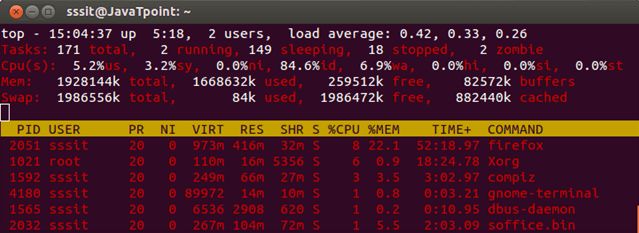
Look at the above snapshot, our output is colored after pressing z.
Now, if you want to change the colors for different areas, press Z (capital Z). it will take you to the menu where you can select different colors for different target.
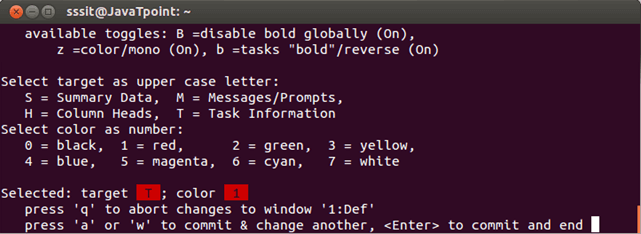
Suppose we want to apply blue color in column heading and magenta color in the task information.
Then we’ll press 4 with H for heading and 5 with T for task information.
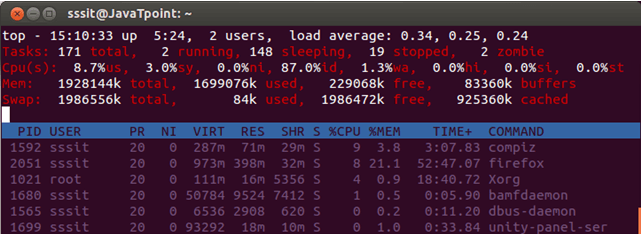
Look at the above snapshot, colors have been changed for their respective target.
Quitting after certain iterations
The top command continuously displays output until you’ll quit by pressing q.
But you can define certain number of iterations after which top command will automatically quit from the terminal.
Syntax:
Example:
top -n 2
With above example, it will show 2 iterations and exit automatical
