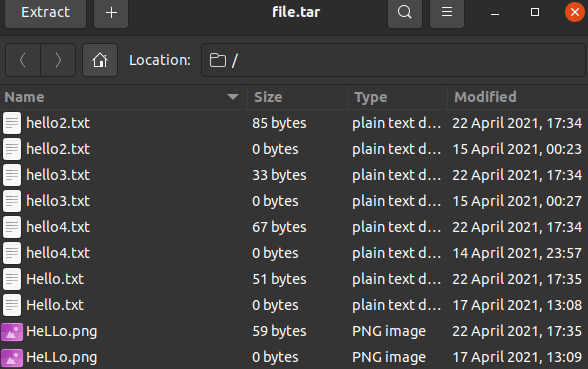
Tar command in Linux
The tar command is short for tape archive in Linux. This command is used for creating Archive and extracting the archive files. In Linux, it is one of the essential commands which facilitate archiving functionality. We can use this command for creating uncompressed and compressed archive files and modify and maintain them as well.
Syntax of tar command:
Options in the tar command
Various options in the tar command are listed below:
- -c: This option is used for creating the archive.
- -f: This option is used for creating an archive along with the provided name of the file.
- -x: This option is used for extracting archives.
- -u: It can be used for adding an archive to the existing archive file.
- -t: It is used for displaying or listing files inside the archived file.
- -A: This option is used for concatenating the archive files.
- -v: It can be used to show verbose information.
- -j: It is used for filtering archive tar files with the help of tbzip.
- -z: It is a zip file and informs the tar command that makes a tar file with the help of gzip.
- -r: This option is used for updating and adding a directory or file in an existing .tar file.
- -W: This option is used for verifying the archive file.
Introduction to Archive File
The archive file can be defined as a file that contains multiple files with metadata. These files are used for collecting more than one data file together in an individual file for easier storage and portability. It can be also used for compressing files to consume less storage space.
Examples of tar command
Some of the important examples which are widely used in tar command are as follows:
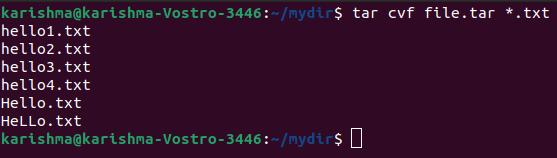
1. Making an uncompressed tar archive with -cvf option
This option makes a tar file known as file.tar. It is the archive of every .txt file inside mydir directory.
The command is as follows:
2. Extracting files through the archive with -xvf option
This option can extract files through archives.
The command is as follows:

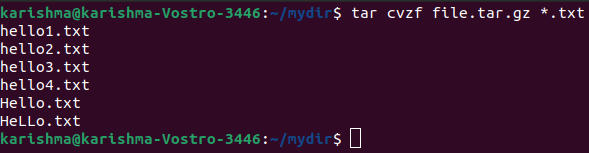
3. gzip compression over tar archive with -z option
This option makes a tar file known as file.tar.gz. It is the archive of every .txt file.
The command is as follows:
4. Extracting the gzip tar archive with -xvzf option
This option can extract the files through file.tar.gz tar archived files.
The command is as follows:

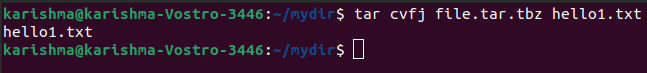
5. Making compressed tar files with the -j option
This option will help us to create and compress archive files. Both decompress and compress takes more time as compared to gzip.
The command is as follows:
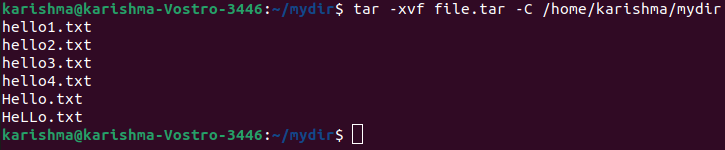
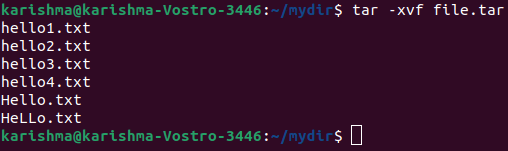
6. Untar single specified directory or file in Linux
This option is used to untar any file in our current directory or inside the specified directory with the -C option.
The command is as follows:
Or,
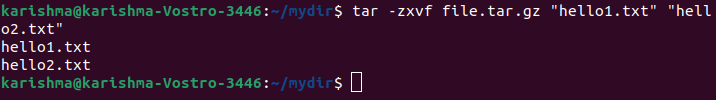
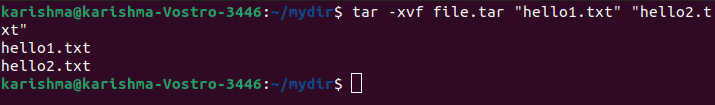
7. Untar multiple .tar.tbz, .tar.gz, .tar files in Linux
This option will help us to untar or extract more than one file from tar.bz2, tar.gz, and a tar archive file.
The example of this option is as follows:

Or,
Or,
8. Check the size of the existing tar.tbz, tar.gz, tar file
The command will help us to show the archive file’s size in kilobytes (KB) which is mentioned above.
The command is as follows:
Or,
Or,

9. Update the existing tar file
In Linux, the command for updating an existing tar file is as follows:
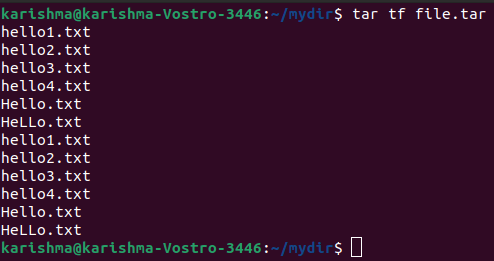
10. Content list and describe the tar file with the tf option
This option will help us to list the whole archive file’s list. Also, we can list particular content inside any tar file.
The command is as follows:
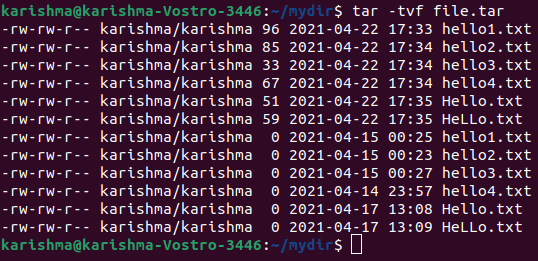
11. View the archive with the -tvf option
In Linux, we can use the -tvf option to view the archive.
The command is as follows:
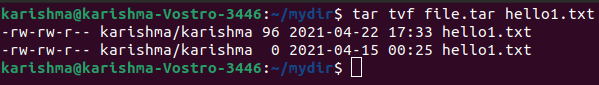
12. Pass the filename as the argument to find a tar file
This option can view the archived files with their information.
The command is as follows:
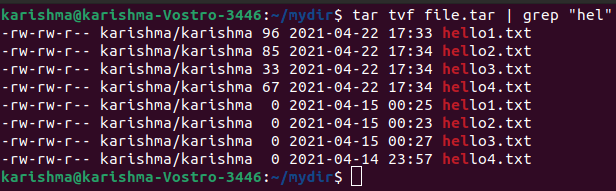
13. Using pipe for throwing ‘grep command’ to search what we are searching for
This option will help us to only list the mentioned image or text in grep through archived files.
The command is as follows:
Or,
Introduction to Wildcards
Alternatively, wildcards are referred to as a wildcard character or wild character in Linux. It is a symbol that is used for representing or replacing multiple characters.
Typically, wildcards are either a question mark (?) which illustrates an individual character or an asterisk (*) which illustrates multiple characters.
Example-
14. Find a .png format image
It will help us for extracting only files along with the .png extension from the file.tar archive. The -wildcards option informs tar for interpreting wildcards in the file name to be extracted.
The name of the file (*.png) is enclosed inside the single quotes for protecting the wildcard (*) through being incorrectly expanded by any shell.
The command is as follows:
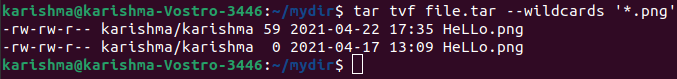
Note: In the above command, the “*” symbol is applied in the position of the name of the file for taking each file available in that specific directory.
15. Delete files from the tar archive
We can use the –delete option for removing files and a tar archive.
The command is as follows:
Example:
Output:

hello1.txt file has been removed from the file.tar archive: