Linux ls command
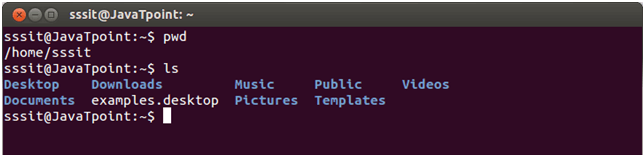
The ls is the list command in Linux. It will show the full list or content of your directory. Just type ls and press the enter key. The whole content will be shown.
Example:
Below, you can see, after entering ls command, we got the whole content list of /home/sssit directory.
Linux ls command options
| ls option | Description |
|---|---|
| ls -a | In Linux, hidden files start with . (dot) symbol and they are not visible in the regular directory. The (ls -a) command will enlist the whole list of the current directory including the hidden files. |
| ls -l | It will show the list in a long list format. |
| ls -lh | This command will show you the file sizes in human readable format. Size of the file is very difficult to read when displayed in terms of byte. The (ls -lh)command will give you the data in terms of Mb, Gb, Tb, etc. |
| ls -lhS | If you want to display your files in descending order (highest at the top) according to their size, then you can use (ls -lhS) command. |
| ls -l – -block-size=[SIZE] | It is used to display the files in a specific size format. Here, in [SIZE] you can assign size according to your requirement. |
| ls -d */ | It is used to display only subdirectories. |
| ls -g or ls -lG | With this you can exclude column of group information and owner. |
| ls -n | It is used to print group ID and owner ID instead of their names. |
| ls –color=[VALUE] | This command is used to print list as colored or discolored. |
| ls -li | This command prints the index number if file is in the first column. |
| ls -p | It is used to identify the directory easily by marking the directories with a slash (/) line sign. |
| ls -r | It is used to print the list in reverse order. |
| ls -R | It will display the content of the sub-directories also. |
| ls -lX | It will group the files with same extensions together in the list. |
| ls -lt | It will sort the list by displaying recently modified filed at top. |
| ls ~ | It gives the contents of home directory. |
| ls ../ | It give the contents of parent directory. |
| ls –version | It checks the version of ls command. |
Linux ls -a command
It will give you the whole list of a directory including the hidden files also. In Linux, hidden files start with a dot (.) and can’t be seen in the regular directory.
Example:
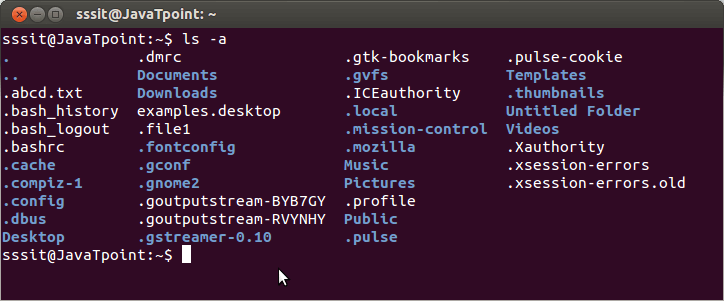
In the above example, you can see the whole list of files, including the hidden files.
Linux ls -l command
The ls command will only display the files. But if you want your files to be displayed in a long list format, then you can use ls -l command.
Example:
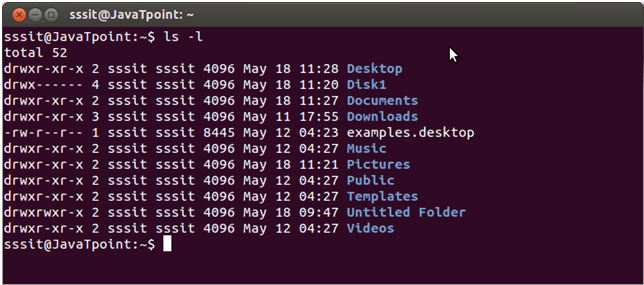
Here, as you can see the list in long list format.
Columns above indicate specific things:
- Column 1 indicates information regarding file permission.
- Column 2 indicates the number of links to the file.
- Column 3 & 4 indicates the owner and group information.
- Column 5 indicayes size of the file in bytes.
- Column 6 shows th date and time on which the file was recently modified.
- Column 7 shows the file or directory name.
Linux ls -l –block-size=[SIZE]
If you want to display the file size of your list in a particular format or size, then you can use this command. Just put the size in place of [SIZE] as per your requirement.
Syntax:
Example:
Let’s see the output below.
![Linux ls -l --block-size=[SIZE]](../wp-content/static/linux/images/linux-ls-l-block-size.png)
Here, all file size has listed in Megabyte.
You can replace [SIZE] with the following measures:
- K = Kilobyte
- M = Megabyte
- G = Gigabyte
- T = Terabyte
- P = Petabyte
- E = Exabyte
- Z = Zettabyte
- Y = Yottabyte
Linux ls -d */
If you only want to display the sub-directories excluding all other files, you can use this command.
Example:
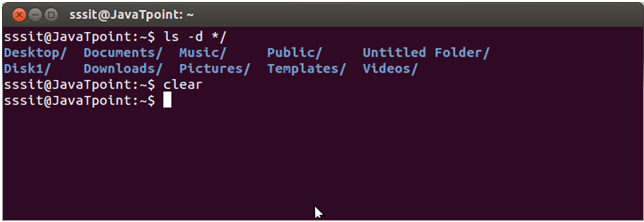
The above result only shows sub-directories excluding all the other files.
Linux ls -g
If you don’t want to display the owner information in your list, then you can exclude this column with the help of this command.
Example:
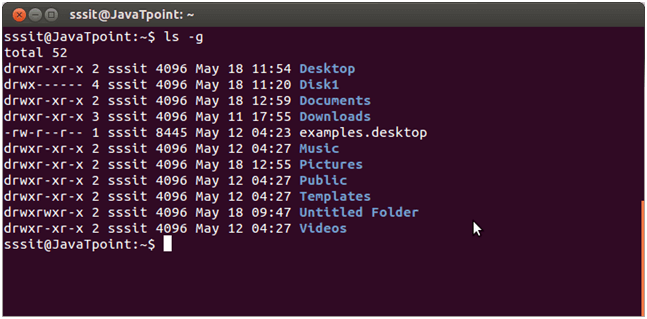
Here owner column is excluded.
Linux ls -lG
If you don’t want to display the group information in your list then you can exclude this column with the help of this command.
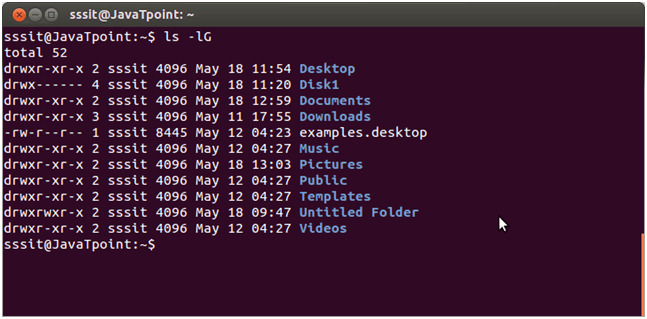
Here group column is excluded.
Linux ls –color=[VALUE]
This command is used to colorize and decolorize the list. If you replace the [VALUE] by ‘auto’, it will display the colored list. But, if you will replace the [VALUE] by ‘never’, it will decolorize the list.
Syntax:
Example:
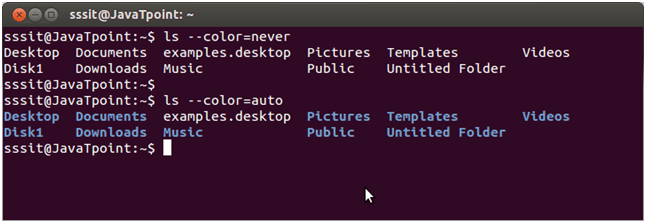
You can easily notice the difference between auto and never command in the above image.
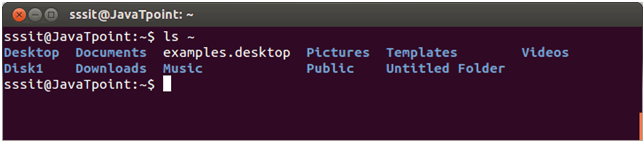
Linux ls ~
Linux ls ~ command shows the contents of the home directory. Let us see the example of ls ~ command.
Example:
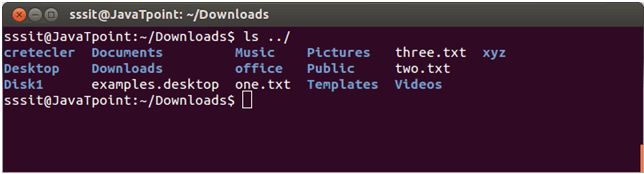
Linux ls ../
This command contains the list of the parent directory.
In the given example, our current directory is Downloads, and by using ls ../ command, we have listed out the content of its parent directory “home directory”.
Example: