Nmap Commands in Kali Linux
Nmap stands for “Network Mapper”. In Kali Linux, Nmap means a utility that is widely used by penetration testers for network discovery and system security audits. Users find Nmap useful for various activities, including network inventory, service uptime tracking, managing schedules, host monitoring, etc. Nmap uses new methods to determine the number of hosts on a network, services provided by the hosts, operating systems they are running on, types of packets or firewalls they use, and several other features. It’s also worth noting that Nmap has been named a security product of the year by Linux Journal, Info World, and other organizations.
How to Use Nmap in Kali Linux?
- Nmap can be used for specific utilities, and specific tasks can be accomplished using the various options available in Nmap. Nmap’s main goal is to protect the network by sniffing traffic and performing extensive network analysis. Detailed network analysis enables the administrator who has built the system for security on the network to get complete information about the packet traffic. Being alert and prepared allows the administrator to speedily respond to attacks.
- The command to scan a single IP address is the initial way to use Nmap. With the help of this, a “threat sniffer” who notices some unusual activity from a single IP can scan to distinguish between false positives and false negatives and hit the target if the IP is notorious. False positives trigger warnings unnecessarily, which can hide any attack. Using utility to differentiate false positives from false negatives will allow false positives to be exposed, keeping the network analyst on their toes to respond to any true positive attack without worrying about false positives.
- Nmap can also be used to scan a host for information that could make it a high-value target on a network that hacking is looking for. For example, attackers target a specific host that comprises financial information.
- In a more advanced situation of scanning an IP address, a user can also use Nmap to scan a range of IP addresses for instances or vulnerabilities via which an attack could be launched. Nmap might also be utilized extensively in a more complex port selection situation. Nmap permits users to scan ports along with the utility, like scanning IP address and range of IP address. With the help of the scanning port, anyone can immediately determine if malware is attacking as malware usually targets a specific port in the host. Now, if we are unsure which ports are malfunctioning, we can scan a range of ports, just like one we had for scanning the range of IP addresses.
Nmap also has the ability to scan the top 100 most commonly used ports, as well as all 65535 ports (this scan will take a lot of time).
What Does Nmap Do?
Nmap is used to offer detailed, real-time information on our networks and the devices connected to them. Nmap’s primary uses can be divided into three categories. First, the program provides detailed information about each IP active on our networks, after which each IP can be scanned. This helps administrators determine whether an IP address is being used by a legitimate service or by a malicious outsider.
Second, Nmap gives us information about the entire network. It can be used to display a list of active hosts and open ports, as well as identify the operating system of all connected devices. This makes it an important aspect of penetration as well as a handy tool for ongoing system monitoring. Nmap can be used with the Metasploit framework to probe and then patch network vulnerabilities.
Third, Nmap is also a useful tool for users who want to secure their personal and corporate websites. Scanning our web server with Nmap, especially if we are hosting our website from home, is effectively replicating how a hacker would attack our site. This method of “attacking” our own site is a very effective means of finding security vulnerabilities.
Nmap is easy to use, and majority of its tools are familiar to system admins from other programs. Nmap has the advantages of combining a variety of these capabilities into a single package, rather than forcing us to switch between other network monitoring tools. You must be familiar with the command-line interface in order to use Nmap.
Although most sophisticated users can write scripts to automate common operations, but basic network monitoring does not require this.
Syntax of Kali Linux Nmap
In Kali Linux, in the context of network analysis or hacking, we call it “sniffing network” a crucial skill and tool for network analysis and hacking undoubtedly the absolute necessity so that we can uncover potential attacks in vulnerable points. Fix them to protect the network and our systems.
The following are some syntaxes which help in “network sniffing”.
1. Syntax for Scanning a Single IP
The following syntax is used to scan a single IP:
Here, <ip address> should be changed with the actual IP address for which the sniff is required.
2. Syntax for Scanning a Single Port
The following syntax is used to scan a single port:
3. Syntax for Scanning Range of Ports
The following syntax is used to scan range of ports:
4. Syntax for Scanning 100 Most Common Ports
The following syntax is used to scan 100 most common ports:
5. Syntax for Scanning a Host
The following syntax is used to scan a host:
Here, <host name> should be changed with the actual host address, which one would need to sniff:
6. Syntax to Scan Using TCP SYN Scan
The following syntax is used to Scan Using TCP SYN Scan:
7. Syntax for Scanning a Range of Ip s
The following syntax is used to scan a range of IPs:
Nmap Commands in Kali Linux
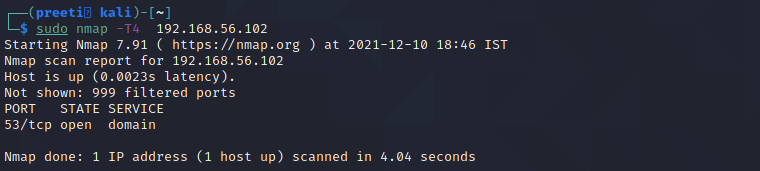
Nmap Command 1: nmap -T4 for Timing
In the scanning process, nmap transmits packets to the target machine in a specific time period (interval). We can use the namp -T switch to increase or decrease the time period. However, the –T option requires an attribute, we should use 1,2,3,4 as needed. T4 has fast speed than T1, T2, and T3.
Syntax:
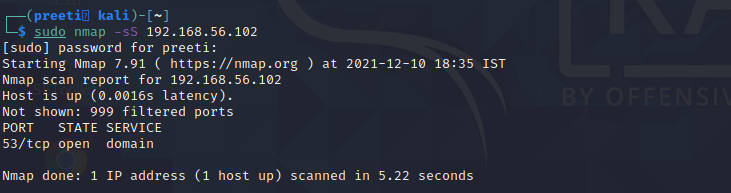
Nmap Command 2: nmap -sS for TCP SYN Scan
It is required privilege access and identifies TCP ports. TCP SYN Scan is a standard method for detecting open ports without going through the Three-way Handshake process. When an open port is spotted, the TCP handshake is reset before accomplishment. Hence this scanning is also called Half Open scanning.
Syntax
Nmap Command 3: nmap -sF for FIN Scan
FIN scan transmits packets with a FIN flag to the target machine; therefore, these frames are abnormal as they are sent to the destination before the Three-way handshaking process can be completed. If there is no active TCP session, then the port is formally closed. If the destination machine’s port is closed then the RST packet in the FIN Scan response is reversed.
Syntax
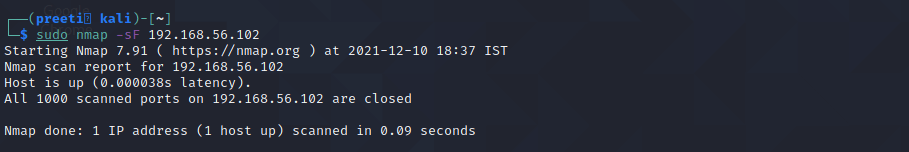
Compared to other nmap scans, an IP Protocol scan has a major difference. It’s looking for other IP protocols utilized by the Target system, such as ICMP, TCP, and UDP. The additional IP protocol, such as EGP, or IGP.
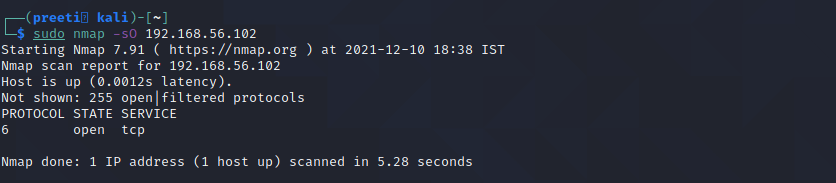
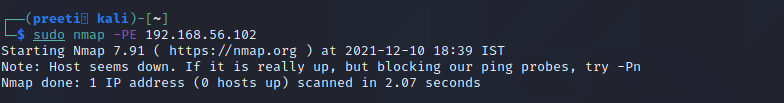
Nmap Command 4: nmap-PE for ICMP Echo Request Ping
The ICMP echo request ping sends an ICMP echo request to the IP address of the destination machine. In the normal type of ICMP echo request, a combination of TCP and ACK pings is sent. Using option -PE, the ICMP echo request can be specified as the nmap ping method without coupling TCP ACK ping.
Syntax
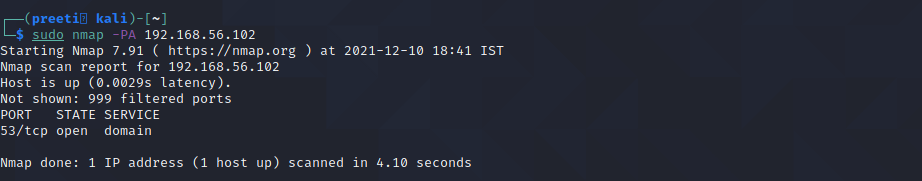
Nmap Command 5: nmap -PA for TCP ACP Ping
Instead of using the default option of both an ICMP echo request and a TCP ACK, the –PA option sends a TCP ACK and discards any ICMP echo requests. This is a decent option when ICMP is not an option due to packet filtering or firewalls.
Syntax
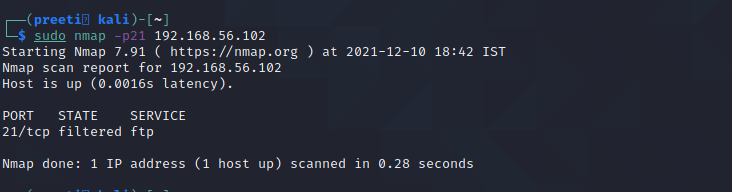
Nmap Command 6: nmap -p for Port Scan
Nmap is mostly used to scan ports; it scans all ports by default, but we can scan single, multiple, or within range protocols.
Single port scan:
Syntax
Multiple scan ports:
Syntax
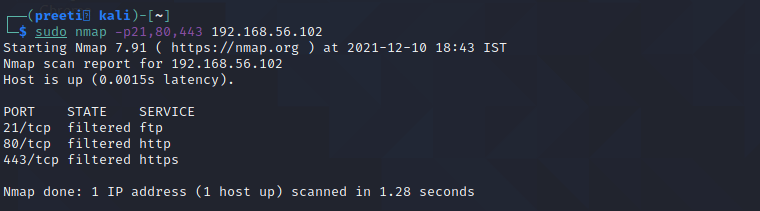
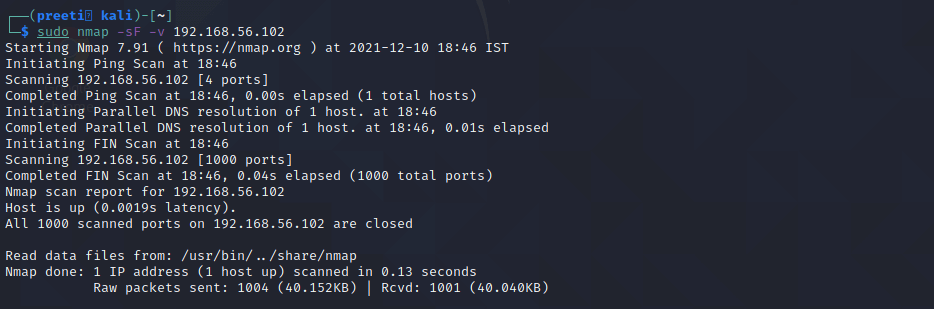
Nmap Command 7: nmap -v for Verbose Mode
The verbose mode of nmap allows us to get more information from the scan output. The verbose option does not affect on what happens during the scan; it only modifies the amount of information that nmap shows on its output.
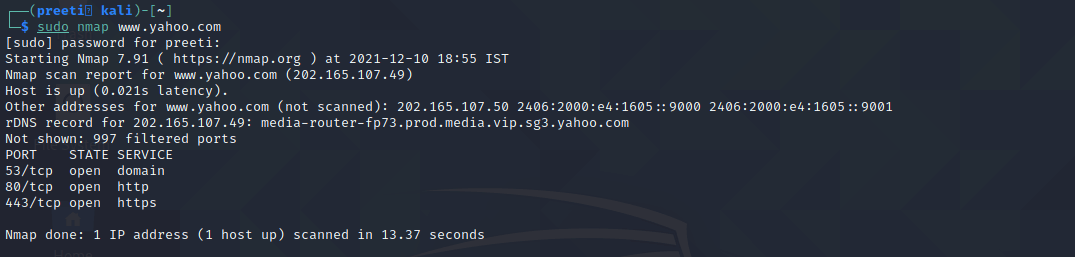
Command 8: nmap for scanning a host
Syntax
Some Other Nmap Commands
Most of the Nmap’s function can be executed with just one command, and the program also uses many “shortcut” commands, which can be used to automate common tasks.
Here is a quick run-down:
1. Ping Scanning
A ping scan returns information on every active IP on our network. This command can be used to perform a ping scan:
2. Scan the Most Popular Ports
This command is especially useful for running Nmap on a home server. It automatically scans various most popular ports for a host. We can use the following command to run this command:
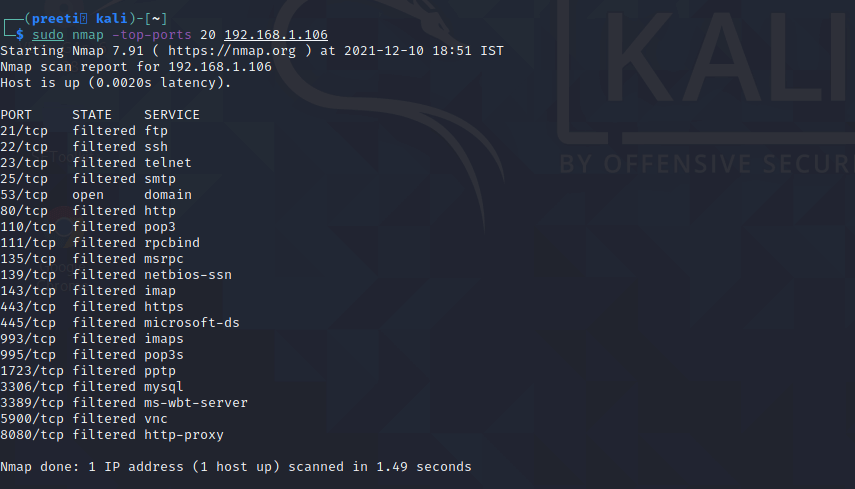
We can replace “20” with the number of ports to scan, and Nmap quickly scans that many ports. It provides a simple output that details the state of the most common ports, allowing us to rapidly determine whether any ports are open needlessly.
3. Disable DNS Name Resolution
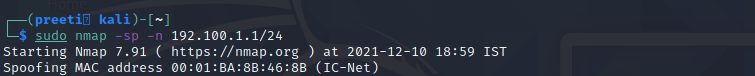
We can also speed up our Nmap scans with the help of the -n parameter to disable reverse DNS resolution. This can be quite handy if we need to scan a huge network. For example, to turn off DNS resolution for the basic ping scan mentioned above, add -n: